Improved rapid diagnostic tests to detect syphilis and yaws: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36180209
- PMCID: PMC9685714
- DOI: 10.1136/sextrans-2022-055546
Improved rapid diagnostic tests to detect syphilis and yaws: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Current rapid tests for syphilis and yaws can detect treponemal and non-treponemal antibodies. We aimed to critically appraise the literature for rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) which can better distinguish an active infection of syphilis or yaws.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis, searching five databases between January 2010 and October 2021 (with an update in July 2022). A generalised linear mixed model was used to conduct a bivariate meta-analysis for the pooled sensitivity and specificity. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic. We used the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) to assess the risk of bias and Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) to evaluate the certainty of evidence.
Results: We included 17 studies for meta-analyses. For syphilis, the pooled sensitivity and specificity of the treponemal component were 0.93 (95% CI: 0.86 to 0.97) and 0.98 (95% CI: 0.96 to 0.99), respectively. For the non-treponemal component, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.90 (95% CI: 0.82 to 0.95) and 0.97 (95% CI: 0.92 to 0.99), respectively. For yaws, the pooled sensitivity and specificity of the treponemal component were 0.86 (95% CI: 0.66 to 0.95) and 0.97 (95% CI: 0.94 to 0.99), respectively. For the non-treponemal component, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.80 (95% CI: 0.55 to 0.93) and 0.96 (95% CI: 0.92 to 0.98), respectively.
Conclusions: RDTs that can differentiate between active and previously treated infections could optimise management by providing same-day treatment and reducing unnecessary treatment.
Prospero registration number: CRD42021279587.
Keywords: DIAGNOSIS; SYPHILIS; YAWS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
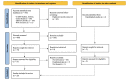




Similar articles
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid diagnostic test for antenatal syphilis screening in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2018 Feb 21;8(2):e018132. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018132. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29467132 Free PMC article.
-
Symptom- and chest-radiography screening for active pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV-negative adults and adults with unknown HIV status.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 23;3(3):CD010890. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010890.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35320584 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Syphilis testing, incidence, and reinfection among gay and bisexual men in Australia over a decade spanning HIV PrEP implementation: an analysis of surveillance data from 2012 to 2022.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024 Aug 24;51:101175. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2024.101175. eCollection 2024 Oct. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024. PMID: 39263009 Free PMC article.
-
The population-level impact of introducing rapid diagnostic tests on syphilis transmission in Canadian arctic communities - a mathematical modeling study.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Jul 20;37:100845. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100845. eCollection 2024 Sep. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 39100242 Free PMC article.
-
Treponema pallidum infection in asymptomatic persons: A puzzling scenario in the Canary Islands (Spain) (2001-2020).PLoS One. 2025 Jul 8;20(7):e0325073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325073. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40627623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Yaws Geneva; 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/yaws [Accessed 30 Oct 2021].
-
- World Health Organization . Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021, 2021. Available: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027077 [Accessed 30 Dec 2021].
-
- World Health Organization . Ending the neglect to attain the sustainable development goals: a road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021–2030; 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240010352 [Accessed 10 Nov 2021].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
