Shoulder replacement: an epidemiological nationwide study from 2009 to 2019
- PMID: 36180858
- PMCID: PMC9526311
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05849-x
Shoulder replacement: an epidemiological nationwide study from 2009 to 2019
Abstract
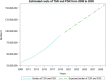
Background: Shoulder replacement (SR) constitutes the gold standard treatment for severe shoulder diseases, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, complex fractures, avascular necrosis and rotator cuff arthropathy. Although several countries have national registries, there is a lack of epidemiological data on SR. Sharing national statistics and correlating those to other countries could be helpful to compare outcomes and costs internationally. This paper aims to evaluate the trend of hospitalizations for SR (both first implants and revisions of anatomical and reverse prosthesis) in Italy from 2009 to 2019, based on the National Hospital Discharge Reports (S.D.O) provided by the Italian National Health Service (INHS). Moreover, the economic impact on the healthcare system of SR and SR revisions was assessed, providing a statistical prediction for the next ten years.
Methods: The data used in this paper were about patients who underwent Total Shoulder Replacement (TSR), Shoulder Hemiarthroplasty (SH) or Revision of shoulder joint replacement (RSR) from 2009 to 2019 in Italy. Information about patients was anonymous and included age, sex, days of hospitalization, procedures and diagnoses codes.
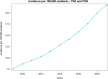
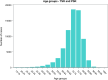
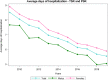
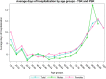
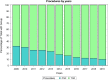
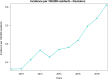
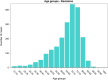
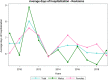
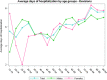
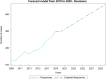
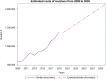
Results: From 2009 to 2019, 73,046 TSR and SH were performed in adult Italian residents, with a cumulative incidence of 13.6 cases per 100,000 adult Italian residents. While, 2,129 revisions of shoulder replacement were performed, with a cumulative incidence of 0.4 cases per 100,000 residents. Overall, females represented the majority of the cases (72.4% of patients who underwent TSR or SH and 59.1% of patients who underwent RSR). From 2009 to 2019, has been assessed an overall cost of 625,638,990€ for TSR or SH procedures in Italy. While, an overall cost of 9,855,141€ for RSR procedures in Italy was calculated.
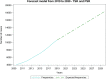
Conclusions: The incidence of SR and RSR is expected to increase in the following years, constituting a burden for the healthcare systems. Overall, in Italy, the females represented the majority of patients. Further prospective studies on this topic in different countries can be con-ducted to make comparisons.
Keywords: Costs; Epidemiology; Italy; Revision of shoulder joint replacement; Shoulder Hemiarthroplasty; Shoulder replacement; Total Shoulder Replacement.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of functional outcomes of reverse shoulder arthroplasty with those of hemiarthroplasty in the treatment of cuff-tear arthropathy: a matched-pair analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 May 15;95(10):910-5. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.L.00302. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013. PMID: 23677358
-
Reverse total shoulder replacement versus anatomical total shoulder replacement for osteoarthritis: population based cohort study using data from the National Joint Registry and Hospital Episode Statistics for England.BMJ. 2024 Apr 30;385:e077939. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-077939. BMJ. 2024. PMID: 38688550 Free PMC article.
-
A review of shoulder replacement surgery.J Perioper Pract. 2012 Nov;22(11):354-9. doi: 10.1177/175045891602201102. J Perioper Pract. 2012. PMID: 23311021 Review.
-
Economic Decision Model Suggests Total Shoulder Arthroplasty is Superior to Hemiarthroplasty in Young Patients with End-stage Shoulder Arthritis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Nov;474(11):2482-2492. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4991-0. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 27457626 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome and risk of revision following shoulder replacement in patients with glenohumeral osteoarthritis.Acta Orthop Suppl. 2014 Jun;85(355):1-23. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2014.922007. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2014. PMID: 24930800 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Lateralization and Distalization on Joint Function after Primary Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;10(12):1409. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10121409. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136000 Free PMC article.
-
High comorbidity burden and low incidence of adverse events in primary shoulder arthroplasty in tertiary care at a university hospital.J Orthop. 2024 Jun 27;58:82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2024.06.040. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39070113
-
Outcomes of Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Were Not Adversely Affected by the COVID-19 Pandemic.Semin Arthroplasty. 2023 Jun 21. doi: 10.1053/j.sart.2023.05.006. Online ahead of print. Semin Arthroplasty. 2023. PMID: 37362778 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical total shoulder arthroplasty revision to reverse shoulder arthroplasty using convertible glenoid: a systematic review of clinical and radiological outcomes.Int Orthop. 2024 Sep;48(9):2411-2419. doi: 10.1007/s00264-024-06188-3. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Int Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38656616
-
The clinical characteristics and demographic distribution of shoulder arthroplasty in China: a nationwide hospital-based study.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025 Jun 4;145(1):332. doi: 10.1007/s00402-025-05948-z. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2025. PMID: 40464986
References
-
- Izquierdo R, Voloshin I, Edwards S, Freehill MQ, Stanwood W, Wiater JM, Watters WC, Goldberg MJ, Keith M, Turkelson CM, et al. American academy of orthopaedic surgeons clinical practice guideline on: the treatment of glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(2):203–205. doi: 10.2106/00004623-201101190-00012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

