Pharmacological mechanism and therapeutic efficacy of Icariside II in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and network pharmacological analysis
- PMID: 36180911
- PMCID: PMC9526298
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-022-03732-9
Pharmacological mechanism and therapeutic efficacy of Icariside II in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and network pharmacological analysis
Abstract
Background and objective: Epimedii has long been used as a traditional medicine in Asia for the treatment of various common diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, cancer, erectile dysfunction, and stroke. Studies have reported the ameliorative effects of Icariside II (ICS II), a major metabolite of Epimedii, on acute ischemic stroke (AIS) in animal models. Based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we conducted a systematic review to evaluate the effects and neuroprotective mechanisms of ICS II on AIS.
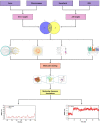
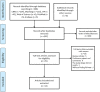
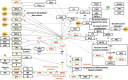
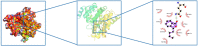
Methods: First, we have searched 6 databases using studies with ICS II treatment on AIS animal models to explore the efficacy of ICS II on AIS in preclinical studies. The literature retrieval time ended on March 8, 2022 (Systematic Review Registration ID: CRD42022306291). There were no restrictions on the language of the search strategy. Systematic review follows the Patient, Intervention, Comparison and Outcome (PICO) methodology and framework. SYCLE's RoB tool was used to evaluate the the risk of bias. In network pharmacology, AIS-related genes were identified and the target-pathway network was constructed. Then, these targets were used in the enrichments of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways and gene ontology (GO). Molecular docking and MD simulation were finally employed between ICS II and the potential target genes.
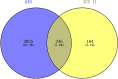
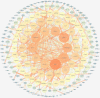
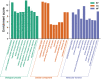
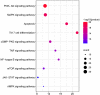
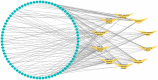
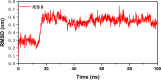
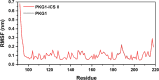
Results: Twelve publications were included describing outcomes of 1993 animals. The literature details, animal strains, induction models, doses administered, duration of administration, and outcome measures were extracted from the 12 included studies. ICS II has a good protective effect against AIS. Most of the studies in this systematic review had the appropriate methodological quality, but some did not clearly state the controlling for bias of potential study. Network pharmacology identified 246 targets with SRC, CTNNB1, HSP90AA1, MAPK1, and RELA as the core target proteins. Besides, 215 potential pathways of ICS II were identified, such as PI3K-Akt, MAPK, and cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. GO enrichment analysis showed that ICS II was significantly enriched in subsequent regulation such as MAPK cascade. Molecular docking and MD simulations showed that ICS II can closely bind with important targets.
Conclusions: ICS II is a promising drug in the treatment of AIS. However, this systematic review reveals key knowledge gaps (i.e., the protective role of ICS II in women) that ICS II must address before it can be used for the treatment of human AIS. Our study shows that ICS II plays a protective role in AIS through multi-target and multi-pathway characteristics, providing ideas for the development of drugs for the treatment of AIS.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Epimedii; Icariside II; Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors; cGMP-PKG signaling pathway.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Wang YJ, Li ZX, Gu HQ, et al. China Stroke Statistics 2019: a report from the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable disease control and prevention, Chinese Center for disease control and prevention and institute for global neuroscience and stroke collaborations. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020;5(3):211–239. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000457. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

