An examination of the association between marital status and prenatal mental disorders using linked health administrative data
- PMID: 36182904
- PMCID: PMC9526285
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-022-05045-8
An examination of the association between marital status and prenatal mental disorders using linked health administrative data
Abstract
Background: International research shows marital status impacts the mental health of pregnant women, with prenatal depression and anxiety being higher among non-partnered women. However, there have been few studies examining the relationship between marital status and prenatal mental disorders among Australian women.
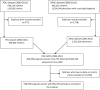
Methods: This is a population-based retrospective cohort study using linked data from the New South Wales (NSW) Perinatal Data Collection (PDC) and Admitted Patients Data Collection (APDC). The cohort consists of a total of 598,599 pregnant women with 865,349 admissions. Identification of pregnant women for mental disorders was conducted using the 10th version International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Australian Modification (ICD-10-AM). A binary logistic regression model was used to estimate the relationship between marital status and prenatal mental disorder after adjusting for confounders.
Results: Of the included pregnant women, 241 (0.04%), 107 (0.02%) and 4359 (0.5%) were diagnosed with depressive disorder, anxiety disorder, and self-harm, respectively. Non-partnered pregnant women had a higher likelihood of depressive disorder (Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) = 2.75; 95% CI: 2.04, 3.70) and anxiety disorder (AOR = 3.16, 95% CI: 2.03, 4.91), compared with partnered women. Furthermore, the likelihood of experiencing self-harm was two times higher among non-partnered pregnant women (AOR = 2.00; 95% CI: 1.82, 2.20) than partnered pregnant women.
Conclusions: Non-partnered marital status has a significant positive association with prenatal depressive disorder, anxiety disorder and self-harm. This suggests it would be highly beneficial for maternal health care professionals to screen non-partnered pregnant women for prenatal mental health problems such as depression, anxiety and self-harm.
Keywords: Anxiety disorder; Data linkage; Depressive disorder; Marital status; Pregnancy; Self-harm.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and determinants of low social support during pregnancy among Australian women: a community-based cross-sectional study.Reprod Health. 2021 Jul 27;18(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01210-y. Reprod Health. 2021. PMID: 34315486 Free PMC article.
-
Comorbid anxiety and depression: Prevalence and associated factors among pregnant women in Arba Minch zuria district, Gamo zone, southern Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 10;16(3):e0248331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248331. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33690693 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The association between social support and antenatal depressive and anxiety symptoms among Australian women.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Oct 22;21(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-04188-4. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 34686140 Free PMC article.
-
Depression and anxiety among pregnant women living with HIV in Kilimanjaro region, Tanzania.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 31;14(10):e0224515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224515. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31671160 Free PMC article.
-
Social determinants of antenatal depression and anxiety among women in South Asia: A systematic review & meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 9;17(2):e0263760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263760. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35139136 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Experiences with discrimination during pregnancy in Canada and associations with depression and anxiety symptoms.Can J Public Health. 2025 Feb;116(1):70-85. doi: 10.17269/s41997-024-00933-2. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Can J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39446296
-
Are virtual services equivalent for mood, anxiety, and bonding? examining a perinatal intensive outpatient program.Arch Womens Ment Health. 2025 Feb;28(1):147-155. doi: 10.1007/s00737-024-01480-y. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 38856949
-
North Carolina Trends in Prenatal Care: The Need for Greater Equity in Prenatal Care Access for Women of Color.J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2025 Jun 24. doi: 10.1007/s40615-025-02524-4. Online ahead of print. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2025. PMID: 40553300
-
Depression and anxiety among pregnant women during COVID 19 pandemic in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Glob Womens Health. 2024 Dec 3;5:1453157. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2024.1453157. eCollection 2024. Front Glob Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39691679 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of postpartum depression on maternal-infant bonding and breastfeeding practices among mothers in Abeokuta, Ogun state.Discov Ment Health. 2024 Oct 25;4(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s44192-024-00104-2. Discov Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 39453530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunkel SC. Psychological science on pregnancy: stress processes, biopsychosocial models, and emerging research issues. Annu Rev Psychol. 2011;62:531–558. - PubMed
-
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, Tunçalp Ö, Moller A-B, Daniels J, et al. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(6):e323–e333. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical