Targeting inflammatory macrophages rebuilds therapeutic efficacy of DOT1L inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36183166
- PMCID: PMC9840147
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.09.019
Targeting inflammatory macrophages rebuilds therapeutic efficacy of DOT1L inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
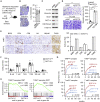
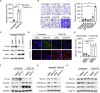
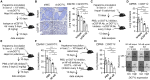
Epigenetic reprogramming is a promising therapeutic strategy for aggressive cancers, but its limitations in vivo remain unclear. Here, we showed, in detailed studies of data regarding 410 patients with human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), that increased histone methyltransferase DOT1L triggered epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediated metastasis and served as a therapeutic target for human HCC. Unexpectedly, although targeting DOT1L in vitro abrogated the invasive potential of hepatoma cells, abrogation of DOT1L signals hardly affected the metastasis of hepatoma in vivo. Macrophages, which constitute the major cellular component of the stroma, abrogated the anti-metastatic effect of DOT1L targeting. Mechanistically, NF-κB signal elicited by macrophage inflammatory response operated via a non-epigenetic machinery to eliminate the therapeutic efficacy of DOT1L targeting. Importantly, therapeutic strategy combining DOT1L-targeted therapy with macrophage depletion or NF-κB inhibition in vivo effectively and successfully elicited cancer regression. Moreover, we found that the densities of macrophages in HCC determined malignant cell DOT1L-associated clinical outcome of the patients. Our results provide insight into the crosstalk between epigenetic reprogramming and cancer microenvironments and suggest that strategies to influence the functional activities of inflammatory cells may benefit epigenetic reprogramming therapy.
Keywords: DOT1L; NF-κB; epigenetic reprogramming; hepatocellular carcinoma; immune microenvironment; inflammation; macrophages; metastasis; therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2022 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures




References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. - PubMed
-
- Nishida J., Momoi Y., Miyakuni K., Tamura Y., Takahashi K., Koinuma D., Miyazono K., Ehata S. Epigenetic remodeling shapes inflammatory renal cancer and neutrophil-dependent metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020;22:465–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

