The role of berberine in Covid-19: potential adjunct therapy
- PMID: 36183284
- PMCID: PMC9526677
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-022-01080-1
The role of berberine in Covid-19: potential adjunct therapy
Abstract
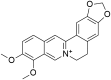
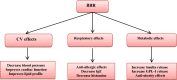
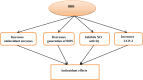
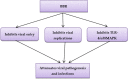
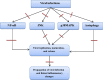
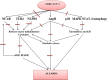
Coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is a global diastrophic disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Covid-19 leads to inflammatory, immunological, and oxidative changes, by which SARS-CoV-2 leads to endothelial dysfunction (ED), acute lung injury (ALI), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multi-organ failure (MOF). Despite evidence illustrating that some drugs and vaccines effectively manage and prevent Covid-19, complementary herbal medicines are urgently needed to control this pandemic disease. One of the most used herbal medicines is berberine (BBR), which has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, and immune-regulatory effects; thus, BBR may be a prospective candidate against SARS-CoV-2 infection. This review found that BBR has anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects with mitigation of associated inflammatory changes. BBR also reduces the risk of ALI/ARDS in Covid-19 patients by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory signaling pathways. In conclusion, BBR has potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiviral effects. Therefore, it can be utilized as a possible anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent. BBR inhibits the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 and attenuates the associated inflammatory disorders linked by the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways. Indeed, BBR can alleviate ALI/ARDS in patients with severe Covid-19. In this sense, clinical trials and prospective studies are suggested to illustrate the potential role of BBR in treating Covid-19.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Antioxidant; Antiviral; Covid-19; Immune-regulatory effects; Inflammatory signaling pathways.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ursolic acid and SARS-CoV-2 infection: a new horizon and perspective.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Oct;30(5):1493-1501. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01038-3. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35922738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitazoxanide and COVID-19: A review.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Nov;49(11):11169-11176. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07822-2. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36094778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small molecule compound berberine as an orally active therapeutic candidate against COVID-19 and SARS: A computational and mechanistic study.FASEB J. 2021 Apr;35(4):e21360. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001792R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33749932 Free PMC article.
-
A Perspective on Erythropoietin as a Potential Adjuvant Therapy for Acute Lung Injury/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Patients with COVID-19.Arch Med Res. 2020 Oct;51(7):631-635. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Arch Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32863034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of β-Blockers on the Sympathetic and Cytokines Storms in Covid-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 11;12:749291. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.749291. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34867978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Receptor-dependent effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) in COVID-19: the black side of the moon.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Oct;478(10):2271-2279. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04658-7. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36652045 Free PMC article.
-
Plausibility of natural immunomodulators in the treatment of COVID-19-A comprehensive analysis and future recommendations.Heliyon. 2023 Jun;9(6):e17478. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17478. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37366526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berberine Inhibits the Inflammatory Response Induced by Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Atopic Eczema Patients via the TNF-α/Inflammation/RAGE Pathways.Cells. 2024 Oct 1;13(19):1639. doi: 10.3390/cells13191639. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404402 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Dietary Supplements to Alleviate Pain Due to Long COVID.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 7;17(7):1287. doi: 10.3390/nu17071287. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40219044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible role of LCZ696 in atherosclerosis: new inroads and perspective.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Aug;479(8):1895-1908. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04816-x. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37526794 Review.
References
-
- Adedara IA, Anao OO, Forcados GE, Awogbindin IO, Agbowo A, Ola-Davies OE, Patlolla AK, Tchounwou PB, Farombi EO. Low doses of multi-walled carbon nanotubes elicit hepatotoxicity in rats with markers of oxidative stress and induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(4):3167–3173. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.112. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adeyemi OS, Afolabi LB, Rotimi DE, Atanu FO, Ofume DS, Ogunleye T, Oluwalana DO, Oluwole TP, Youssef A, Mostafa-Hedeab G. Differential immunomodulatory potential of silver nanoparticles and effect on the kynurenine pathway in male wistar rats. J Nanomater. 2022;2022:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2022/9883142. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
