The role of berberine in Covid-19: potential adjunct therapy
- PMID: 36183284
- PMCID: PMC9526677
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-022-01080-1
The role of berberine in Covid-19: potential adjunct therapy
Abstract
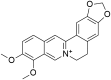
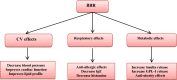
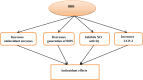
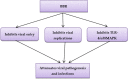
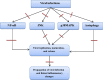
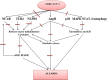
Coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is a global diastrophic disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Covid-19 leads to inflammatory, immunological, and oxidative changes, by which SARS-CoV-2 leads to endothelial dysfunction (ED), acute lung injury (ALI), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and multi-organ failure (MOF). Despite evidence illustrating that some drugs and vaccines effectively manage and prevent Covid-19, complementary herbal medicines are urgently needed to control this pandemic disease. One of the most used herbal medicines is berberine (BBR), which has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, and immune-regulatory effects; thus, BBR may be a prospective candidate against SARS-CoV-2 infection. This review found that BBR has anti-SARS-CoV-2 effects with mitigation of associated inflammatory changes. BBR also reduces the risk of ALI/ARDS in Covid-19 patients by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory signaling pathways. In conclusion, BBR has potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiviral effects. Therefore, it can be utilized as a possible anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent. BBR inhibits the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 and attenuates the associated inflammatory disorders linked by the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways. Indeed, BBR can alleviate ALI/ARDS in patients with severe Covid-19. In this sense, clinical trials and prospective studies are suggested to illustrate the potential role of BBR in treating Covid-19.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Antioxidant; Antiviral; Covid-19; Immune-regulatory effects; Inflammatory signaling pathways.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adedara IA, Anao OO, Forcados GE, Awogbindin IO, Agbowo A, Ola-Davies OE, Patlolla AK, Tchounwou PB, Farombi EO. Low doses of multi-walled carbon nanotubes elicit hepatotoxicity in rats with markers of oxidative stress and induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(4):3167–3173. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.112. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adeyemi OS, Afolabi LB, Rotimi DE, Atanu FO, Ofume DS, Ogunleye T, Oluwalana DO, Oluwole TP, Youssef A, Mostafa-Hedeab G. Differential immunomodulatory potential of silver nanoparticles and effect on the kynurenine pathway in male wistar rats. J Nanomater. 2022;2022:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2022/9883142. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
