Effect of brewing conditions on the chemical and sensory profiles of milk tea
- PMID: 36185102
- PMCID: PMC9516450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100453
Effect of brewing conditions on the chemical and sensory profiles of milk tea
Abstract
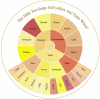
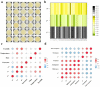
The brewing conditions of beverage milk tea determine the taste of milk tea. This study investigated the changes in sensory characteristics and small molecule compounds in milk tea made from large-leaf yellow tea under different brewing conditions by sensory analysis, colorimeter, and LC-MS. The results show that the tea to milk ratio is the most important process affecting the taste, and the color values of b* (+yellow, - blue) can be used to evaluate the taste of milk tea made from large leaf yellow tea. The composition of small molecular compounds is affected by tea to milk ratio, which can change the taste of milk tea. l-cysteine and 8-methylsulfinyloctyl glucosinolate are significantly positively correlated with taste by metabolomics analysis. l-cysteine was used to verify the analysis results by LC-MS. The total acceptance of milk tea is improved by adding l-cysteine at a low level (0.025-0.035 mM).
Keywords: Color; Large leaf yellow tea; Milk tea; Non-targeted metabolomics; Response surface methodology; l-cysteine.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of brewing conditions on the phytochemical composition, sensory qualities and antioxidant activity of green tea infusion: A study using response surface methodology.Food Chem. 2018 Dec 15;269:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.130. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30100430
-
Influence of brewing conditions on taste components in Fuding white tea infusions.J Sci Food Agric. 2017 Jul;97(9):2826-2833. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8111. Epub 2016 Dec 1. J Sci Food Agric. 2017. PMID: 27786360
-
LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Reveals the Chemical Changes of Polyphenols during High-Temperature Roasting of Large-Leaf Yellow Tea.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 May 15;67(19):5405-5412. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05062. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30485095
-
Yellow tea: more than turning green leaves to yellow.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(22):7836-7853. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2193271. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37009836 Review.
-
Review: the effect of light on the key pigment compounds of photosensitive etiolated tea plant.Bot Stud. 2021 Dec 11;62(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40529-021-00329-2. Bot Stud. 2021. PMID: 34897570 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
College Students' Preferences for Milk Tea: Results from a Choice Experiment.Foods. 2023 Apr 1;12(7):1491. doi: 10.3390/foods12071491. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37048313 Free PMC article.
-
1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Machine-Learning Algorithm for Origin Recognition of Chinese Famous Green Tea Longjing Tea.Foods. 2024 Aug 27;13(17):2702. doi: 10.3390/foods13172702. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39272468 Free PMC article.
-
Process-Induced Molecular-Level Protein-Carbohydrate-Polyphenol Interactions in Milk-Tea Blends: A Review.Foods. 2024 Aug 8;13(16):2489. doi: 10.3390/foods13162489. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bennett R.N., Mellon F.A., Kroon P.A. Screening crucifer seeds as sources of specific intact glucosinolates using ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography negative ion electrospray mass spectrometry. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2004;52(3):428–438. doi: 10.1021/jf030530p. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhagat A.R., Delgado A.M., Issaoui M., Chammem N., Fiorino M., Pellerito A., Natalello S. Review of the role of fluid dairy in delivery of polyphenolic compounds in the diet: Chocolate milk, coffee beverages, Matcha green tea, and beyond. Journal of AOAC International. 2019;102(5):1365–1372. doi: 10.1093/jaoac/102.5.1365. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

