Bibliometric analysis for economy in COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 36185135
- PMCID: PMC9509534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10757
Bibliometric analysis for economy in COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
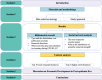
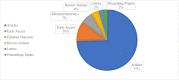
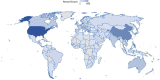
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, various fields have been damaged to varying degrees, especially in the economic field. According to a comprehensive study of bibliometrics and content analysis, this paper aims at summarizing studies related to the development of the economic field during the COVID-19 epidemic. We search in Web of Science Core Collection using the subjects such as "economics", "economy", "economic", "financial", and then 2274 related documents are collected, which are published from 2020 to 2022. First, this paper uses the mixed qualitative and quantitative analysis methods to analyze the publication status of the countries, institutions, and authors, respectively, and conducts the document co-citation analysis by CiteSpace software. The results showed that the most popular journal is Sustainability, and the most productive research institutions, countries, and authors are primarily located in North American and European countries. Then, it makes an in-depth study of the cooperative network. With the support of Gephi software, this paper employs the social network analysis method to analyze the situation of the country/region cooperation and institutional cooperation. Finally, the content analysis of the related studies is presented to further explore the current challenges. On this basis, this paper analyzes the economic development in the post-epidemic era and draws some conclusions, which provide some references for scholars interested in this field.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; COVID-19; Content analysis; Economy.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


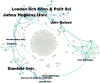

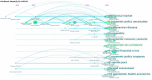
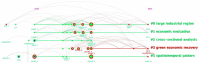
Similar articles
-
Knowledge Structure and Emerging Trends of Telerehabilitation in Recent 20 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 20;10:904855. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.904855. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35795695 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific mapping of hotspots and trends of post and core research based on the Web of Science: A bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 19;10(1):e23786. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23786. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38226214 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Publication trends of research on COVID-19 and host immune response: A bibliometric analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 8;10:939053. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.939053. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36003630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prediction of Infectious Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Aug 27;17(17):6218. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176218. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32867133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Examining the influence of financial inclusion on investment decision: A bibliometric review.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 5;10(3):e25779. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25779. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38356575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of research hotspots in COVID-19 genomics based on citespace software: Bibliometric analysis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Dec 12;12:1060031. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1060031. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36579345 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the research landscape: Mapping frontiers and hot spots in anti-cancer research using bibliometric analysis and research network pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 7;14:1256188. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1256188. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37745055 Free PMC article.
-
Project portfolio risk management. Bibliometry and collaboration Scientometric domain analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 22;9(9):e19136. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19136. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic evaluation and review of Germany renewable energy research: A bibliometric study from 2008 to 2023.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 24;10(15):e34933. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34933. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39166091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albu L., Preda C.I., Lupu R., Dobrota C., Călin G.M., Boghicevici C.M. Estimates of dynamics of the COVID-19 pandemic and of its impact on the economy. Rom. J. Econ. Forecast. 2020;23(2):5–17.
-
- Alshater M.M., Atayah O.F., Khan A. What Do we know about business and economics research during COVID-19: a bibliometric review. Econ. Res.-Ekonomska Istraživanja. 2022;35(1):1884–1912.
-
- Baker S.R., Bloom N., Davis S.J., Kost K., Sammon M., Viratyosin T., Pontiff J. The unprecedented stock market reaction to COVID-19. Rev. Asset Pricing Stud. 2020;10(4):742–758.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

