Cbl-b restrains priming of pathogenic Th17 cells via the inhibition of IL-6 production by macrophages
- PMID: 36185364
- PMCID: PMC9523381
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105151
Cbl-b restrains priming of pathogenic Th17 cells via the inhibition of IL-6 production by macrophages
Abstract
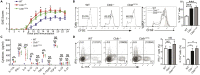
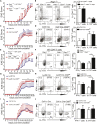
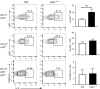
E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b is involved in the maintenance of a balance between immunity and tolerance. Mice lacking Cbl-b are highly susceptible to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a Th17-mediated autoimmune disease. However, how Cbl-b regulates Th17 cell responses remains unclear. In this study, utilizing adoptive transfer and cell type-specific Cblb knockout strains, we show that Cbl-b expression in macrophages, but not T cells or dendritic cells (DCs), restrains the generation of pathogenic Th17 cells and the development of EAE. Cbl-b inhibits IL-6 production by macrophages that is induced by signaling from CARD9-dependent C-type lectin receptor (CLR) pathways, which directs T cells to generate pathogenic Th17 cells. Therefore, our data unveil a previously unappreciated function for Cbl-b in the regulation of pathogenic Th17 responses.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Immune response; Immunology.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso R., Fernandez-Fernandez A.M., Pisa D., Carrasco L. Multiple sclerosis and mixed microbial infections. Direct identification of fungi and bacteria in nervous tissue. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018;117:42–61. - PubMed
-
- Bachmaier K., Krawczyk C., Kozieradzki I., Kong Y.Y., Sasaki T., Oliveira-dos-Santos A., Mariathasan S., Bouchard D., Wakeham A., Itie A., et al. Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cbl-b. Nature. 2000;403:211–216. - PubMed
-
- Bergholdt R., Taxvig C., Eising S., Nerup J., Pociot F. CBLB variants in type 1 diabetes and their genetic interaction with CTLA4. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005;77:579–585. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

