Underwater instant adhesion mechanism of self-assembled amphiphilic hemostatic granular hydrogel from Andrias davidianus skin secretion
- PMID: 36185384
- PMCID: PMC9519738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105106
Underwater instant adhesion mechanism of self-assembled amphiphilic hemostatic granular hydrogel from Andrias davidianus skin secretion
Abstract
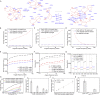
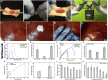
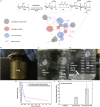
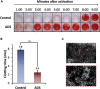
The widespread use of biological tissue adhesives for tissue repair is limited by their weak adhesion in a wet environment. Herein, we report the wet adhesion mechanism of a dry granular natural bioadhesive from Andrias davidianus skin secretion (ADS). Once contacting water, ADS granules self-assemble to form a hydrophobic hydrogel strongly bonding to wet substrates in seconds. ADS showed higher shear adhesion than current commercial tissue adhesives and an impressive 72-h underwater adhesion strength of ∼47kPa on porcine skin tissue. The assembled hydrogel in water maintained a dissipation energy of ∼8 kJ/m3, comparable to the work density of muscle, exhibiting its robustness. Unlike catechol adhesion mechanism, ADS wet adhesion mechanism is attributed to water absorption by granules, and the unique equilibrium of protein hydrophobicity, hydrogen bonding, and ionic complexation. The in vivo adhesion study demonstrated its excellent wet adhesion and hemostasis performance in a rat hepatic and cardiac hemorrhage model.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Materials chemistry; Materials science.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mussel foot protein inspired tough tissue-selective underwater adhesive hydrogel.Mater Horiz. 2021 Mar 1;8(3):997-1007. doi: 10.1039/d0mh01231a. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Mater Horiz. 2021. PMID: 34821330
-
Mussel Foot Protein-Inspired Adhesive Tapes with Tunable Underwater Adhesion.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Aug 28;16(34):45550-45562. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c09709. Epub 2024 Aug 15. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39145483
-
Tough Wet Adhesion of Hydrogen-Bond-Based Hydrogel with On-Demand Debonding and Efficient Hemostasis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Aug 10;14(31):36166-36177. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c10202. Epub 2022 Jul 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 35899775
-
Bioinspired Underwater Adhesives.Adv Mater. 2021 Nov;33(44):e2102983. doi: 10.1002/adma.202102983. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 34532910 Review.
-
Cation-π Interactions and Their Contribution to Mussel Underwater Adhesion Studied Using a Surface Forces Apparatus: A Mini-Review.Langmuir. 2019 Dec 3;35(48):16002-16012. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01976. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Langmuir. 2019. PMID: 31423790 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinspired hierarchical porous tough adhesive to promote sealing of high-pressure bleeding.Bioact Mater. 2024 Nov 16;45:88-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.11.003. eCollection 2025 Mar. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39634058 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet Vesicles Synergetic with Biosynthetic Cellulose Aerogels for Ultra-Fast Hemostasis and Wound Healing.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Jul;13(17):e2304523. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202304523. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38345186 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of skin wound healing by giant salamander skin mucus gel wrapped with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via affecting integrin family molecules.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 May 3;16(9):7902-7914. doi: 10.18632/aging.205792. Epub 2024 May 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38709270 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in biomimetic hemostatic materials.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Feb 24;19:100592. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100592. eCollection 2023 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 36936399 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barton A.F.M. Second edition. CRC Press; 2017. CRC Handbook of Solubility Parameters and Other Cohesion Parameters.
-
- Bouten P.J., Zonjee M., Bender J., Yauw S.T., van Goor H., van Hest J.C., Hoogenboom R. The chemistry of tissue adhesive materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014;39:1375–1405. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2014.02.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

