Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
- PMID: 36185402
- PMCID: PMC9482421
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2022-0468
Neuroprotective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes against the paraquat-induced oxidative brain damage in rats
Abstract
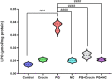
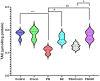
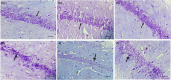
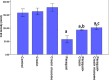
Paraquat (PQ) is a nonselective herbicide that induces oxidative reactions and multiple-organ failure on exposure. Crocin, a carotenoid obtained from saffron, has demonstrated many therapeutic effects against neural conditions because of its antioxidant properties. In this study, 30 male Wistar rats were divided into 6 groups to evaluate the protective effects of crocin and crocin-loaded niosomes (NC) against PQ in the brain. The levels of total antioxidant capacity (TAC), lipid peroxidation (LPO), total thiol groups (TTG), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) activity were measured as the markers of redox status. Histopathological changes in the CA1 region of the hippocampus were evaluated by cresyl violet staining. Results indicated that both crocin and NC were able to attenuate the adverse effects of PQ at the histopathological level, which was following the changes in LPO (P < 0.0001), TAC (P < 0.01), and TTG (P < 0.05) level. The activity of CAT (P < 0.01) and SOD (P < 0.01) could be restored either by crocin or NC. Also, results indicated that nanoformulation of crocin in niosomes appears to be more promising. In conclusion, both crocin and NC showed favourable effects of PQ in the brain of rats, and were determined to be excellent agents to prevent acute toxicities of PQ. Furthermore, these two compounds can be known to provide neuroprotection.
Keywords: brain; crocin-loaded niosomes; oxidative stress; paraquat; rats.
© 2022 Afsoon Daneshvar et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antioxidative Effects of Crocin-loaded Noisome in Paraquat-induced Oxidative Stress in Lung Rat.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun 4. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01788-1. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40468138
-
Crocin and Nano-Crocin Mitigate Paraquat Hepatotoxicity by Modulating Expression of Genes Involved in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2025 Jan 30. doi: 10.2174/0122117385323941241211084423. Online ahead of print. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39901556
-
Nanocrocin Protective Effects on Paraquat-Induced Oxidative Stress in the MRC-5 Cell Line.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2024 Apr;39(2):283-290. doi: 10.1007/s12291-022-01096-y. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38577135 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of oxidative stress status in the kidney tissue of male rats treated with paraquat and nanoparaquat.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):389. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83156-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747891 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of N-acetylcystein loaded niosomes on liver function in paraquat-induced acute poisoning.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2019 Oct;160:146-153. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31519249
Cited by
-
Modulating effects of crocin on lipids and lipoproteins: Mechanisms and potential benefits.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 3;10(7):e28837. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28837. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38617922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential therapeutic effects of crocin.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;397(10):7395-7420. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03131-6. Epub 2024 May 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38758225 Review.
-
Antioxidative Effects of Crocin-loaded Noisome in Paraquat-induced Oxidative Stress in Lung Rat.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun 4. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01788-1. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40468138
-
A comprehensive literature review on the effects of saffron and its bioactive components on traumatic brain injury (TBI).Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):7785-7800. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03868-8. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39928149 Review.
References
-
- Amirshahrokhi K, Bohlooli S. Effect of methylsulfonylmethane on paraquat-induced acute lung and liver injury in mice. Inflammation. 2013;36(5):1111–21. - PubMed
-
- Nunes ME, Müller TE, Braga MM, Fontana BD, Quadros VA, Marins A, et al. Chronic treatment with paraquat induces brain injury, changes in antioxidant defenses system, and modulates behavioral functions in zebrafish. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(6):3925–34. - PubMed
-
- McCormack AL, Atienza JG, Johnston LC, Andersen JK, Vu S, Di Monte DA. Role of oxidative stress in paraquat‐induced dopaminergic cell degeneration. J Neurochem. 2005;93(4):1030–7. - PubMed
-
- Bateman D. Pharmacological treatments of paraquat poisoning. Hum Toxicol. 1987;6(1):57–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
