Expression patterns of the poplar NF-Y gene family in response to Alternaria alternata and hormone treatment and the role of PdbNF-YA11 in disease resistance
- PMID: 36185440
- PMCID: PMC9523018
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.956271
Expression patterns of the poplar NF-Y gene family in response to Alternaria alternata and hormone treatment and the role of PdbNF-YA11 in disease resistance
Abstract
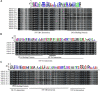
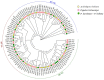
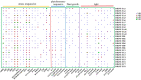
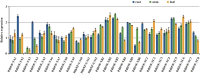
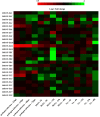
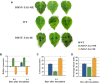
Plant nuclear factor-Y (NF-Y) transcription factors (TFs) are key regulators of growth and stress resistance. However, the role of NF-Y TFs in poplar in response to biotic stress is still unclear. In this study, we cloned 26 PdbNF-Y encoding genes in the hybrid poplar P. davidiana × P. bollena, including 12 PdbNF-YAs, six PdbNF-YBs, and eight PdbNF-YCs. Their physical and chemical parameters, conserved domains, and phylogeny were subsequently analyzed. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network showed that the three PdbNF-Y subunits may interact with NF-Y proteins belonging to two other subfamilies and other TFs. Tissue expression analysis revealed that PdbNF-Ys exhibited three distinct expression patterns in three tissues. Cis-elements related to stress-responsiveness were found in the promoters of PdbNF-Ys, and most PdbNF-Ys were shown to be differentially expressed under Alternaria alternata and hormone treatments. Compared with the PdbNF-YB and PdbNF-YC subfamilies, more PdbNF-YAs were significantly induced under the two treatments. Moreover, loss- and gain-of-function analyses showed that PdbNF-YA11 plays a positive role in poplar resistance to A. alternata. Additionally, RT‒qPCR analyses showed that overexpression and silencing PdbNF-YA11 altered the transcript levels of JA-related genes, including LOX, AOS, AOC, COI, JAZ, ORCA, and MYC, suggesting that PdbNF-YA11-mediated disease resistance is related to activation of the JA pathway. Our findings will contribute to functional analysis of NF-Y genes in woody plants, especially their roles in response to biotic stress.
Keywords: JA signal; NF-Y transcription factor; disease resistance; expression pattern; poplar.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Ma, Wang, Cui, Han, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multiple NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors respond to abiotic stress in Brassica napus L.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 30;9(10):e111354. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111354. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25356551 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptomic and transgenic analyses reveal potential mechanisms of poplar resistance to Alternaria alternata infection.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Aug 25;22(1):413. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03793-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36008749 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, Structural Characterization and Gene Expression Analysis of Members of the Nuclear Factor-Y Family in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under Dehydration and Abscisic Acid Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 23;19(11):3290. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113290. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30360493 Free PMC article.
-
Plant NF-Y transcription factors: Key players in plant-microbe interactions, root development and adaptation to stress.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 May;1860(5):645-654. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 27939756 Review.
-
The promiscuous life of plant NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors.Plant Cell. 2012 Dec;24(12):4777-92. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.105734. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 23275578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alam M. M., Tanaka T., Nakamura H., Ichikawa H., Kobayashi K., Yaeno T., et al. (2015). Overexpression of a rice heme activator protein gene (OsHAP2E) confers resistance to pathogens, salinity and drought, and increases photosynthesis and tiller number. Plant Biotechnol. J. 13, 85–96. 10.1111/pbi.12239 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

