An Integrated Analysis of Inflammatory Endotypes and Clinical Characteristics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
- PMID: 36185639
- PMCID: PMC9518682
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S377301
An Integrated Analysis of Inflammatory Endotypes and Clinical Characteristics in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Abstract
Objective: Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is mainly characterised by type 1 (T1), type 2 (T2) and type 3 (T3) inflammatory endotypes. However, correlations between inflammatory endotypes and clinical features in CRSwNP have not been demonstrated sufficiently. This study aimed to determine the endotype-phenotype associations in CRSwNP.
Methods: Clinical data of 31 control subjects and 106 CRSwNP patients were analysed. Interferon (IFN)-γ (T1), Charcot-Leyden crystal galectin (CLC) (T2) and Interleukin (IL)-17A (T3) were used as biomarkers to identify the inflammatory endotypes.
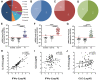
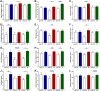
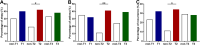
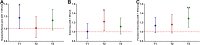
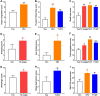
Results: The mRNA expression level of IFN-γ was positively correlated with IL-17A (r = 0.817; P < 0.0001). Headache/facial pain (P = 0.039) was associated with T1 endotype. Smell loss (P = 0.025) was associated with T2 endotype. Purulent rhinorrhea (P = 0.001) was associated with T3 endotype. Atopy (P = 0.030), asthma (P = 0.005) and recurrence (P = 0.022) were more frequent in T2 endotype. Total Symptom Scores (TSS) of T2 (P < 0.001) and T3 (P = 0.009) endotype were higher than non-T2 and non-T3, respectively. Sino Nasal Outcome Test-22 (SNOT-22) total scores of T3 (P = 0.054) endotype were higher than non-T3.
Conclusion: Identifications of endotype-phenotype associations are useful in clinical diagnoses and targeted therapies for patients with CRSwNP.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; diagnosis; endotype; phenotype; therapy.
© 2022 Hao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in relation to this work and declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

