Type I interferon induces cancer stem cells-mediated chemotherapy resistance
- PMID: 36185803
- PMCID: PMC9518997
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2127274
Type I interferon induces cancer stem cells-mediated chemotherapy resistance
Abstract
In a recent study in Nature Immunology, Musella et al. demonstrate that suboptimal type I interferon (IFN-I) signaling in tumors undergoing immunogenic cell death (ICD) facilitates the accumulation of cancer stem cells (CSCs) by triggering the epigenetic regulator lysine demethylase 1B (KDM1B). KDM1B stands out as a promising target for the development of novel strategies to improve anti-cancer responses driven by ICD.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; KDM1B; cancer stem cells; epigenetic immune escape; immunogenic cell death; interferon type I.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have nothing to disclose pertaining to this work.
Figures
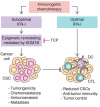
Comment on
-
Type I IFNs promote cancer cell stemness by triggering the epigenetic regulator KDM1B.Nat Immunol. 2022 Sep;23(9):1379-1392. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01290-3. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36002648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boukhaled GM, Gadalla R, Elsaesser HJ, Abd-Rabbo D, Quevedo R, Yang SYC, Guo M, Wang BX, Noamani B, Gray D, et al. Pre-encoded responsiveness to type I interferon in the peripheral immune system defines outcome of PD1 blockade therapy. Nat Immunol. 2022;23(8):1273–1283. doi:10.1038/s41590-022-01262-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
