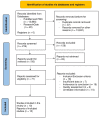
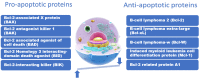
A Systematic Review of Apoptosis in Correlation With Cancer: Should Apoptosis Be the Ultimate Target for Cancer Treatment?
- PMID: 36185861
- PMCID: PMC9514374
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.28496
A Systematic Review of Apoptosis in Correlation With Cancer: Should Apoptosis Be the Ultimate Target for Cancer Treatment?
Abstract
Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy has become increasingly popular, and there has been an increasing debate on whether apoptosis should be one of the main targets of therapy in cancer management. This study demonstrates the definition of apoptosis, the signaling pathways, and the pathogenesis behind it. We also show the correlation between apoptosis and cancer and how cancer can evade apoptosis to develop resistance to therapy. In addition, we illustrate the efficacy of adding pro-apoptotic therapy to conventional radio-chemotherapy cancer treatment. A systematic review was conducted using PubMed, PubMed Central (PMC), and ResearchGate, including papers written in English, focusing on adult and geriatric populations, in literature reviews, systematic reviews, and randomized controlled trials published in the last 25 years with relevance to the question. Based on the findings of this review, we conclude that apoptosis is a very sophisticated programmed cellular death with many signaling pathways. Its evasion should be considered one of the hallmarks of cancer and is responsible for multiple drug resistance (MDR) to cancer therapy. Targeting apoptosis seems promising, especially if combined with radio-chemotherapy.
Keywords: anti-apoptotic therapy; apoptosis; cancer; multiple drug resistance; regulated cell death.
Copyright © 2022, Abaza et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer and Apoptosis.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2543:191-210. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2553-8_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36087269
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
KRAS Testing for Anti-EGFR Therapy in Advanced Colorectal Cancer: An Evidence-Based and Economic Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(25):1-49. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074403 Free PMC article.
-
Present and potential future adjuvant issues in high-grade astrocytic glioma treatment.Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2009;34:3-35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-78741-0_1. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2009. PMID: 19368079 Review.
-
Targeting apoptotic signaling pathways in human lung cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010 Sep;10(6):566-74. doi: 10.2174/156800910791859461. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20482489 Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming the therapeutic limitations of EZH2 inhibitors in Burkitt's lymphoma: a comprehensive study on the combined effects of MS1943 and Ibrutinib.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 11;13:1252658. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1252658. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37752998 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylases in the regulation of cell death and survival mechanisms in resistant BRAF-mutant cancers.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Jan 25;8:6. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.125. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39935431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nerolidol, Bioactive Compound Suppress Growth of HCT-116 Colorectal Cancer Cells Through Cell Cycle Arrest and Induction of Apoptosis.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;196(3):1365-1375. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04612-9. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37395945
-
Metformin and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: implications for cancer, cardiovascular, and central nervous system diseases.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1035-1055. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03358-3. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39225830 Review.
-
Targeting Apoptotic Pathway of Cancer Cells with Phytochemicals and Plant-Based Nanomaterials.Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 18;13(2):194. doi: 10.3390/biom13020194. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Programmed cell death and the immune system. Nagata S, Tanaka M. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17:333–340. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources