Calcifying fibrous tumor
- PMID: 36186113
- PMCID: PMC9524383
- DOI: 10.4322/acr.2021.400
Calcifying fibrous tumor
Abstract
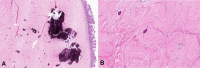
Calcifying fibrous tumor is a rare benign mesenchymal neoplasm. The etiology and pathogenesis of this tumor are uncertain. It has wide anatomical distribution. The tumor is most commonly found in the soft tissues of the extremities in younger individuals. However, in middle-aged patients, it tends to affect the visceral locations more commonly. In visceral location, it can mimic aggressive lesions clinically. The purpose of this report is to describe a case of calcifying fibrous tumor in a 71-year-old female with a history of breast carcinoma who was found to have an incidental small bowel mass on her follow-up. Clinically and radiologically, the mass was suspicious for either metastatic disease or gastrointestinal stromal tumor. The patient underwent open small bowel resection, and a 6.5 cm segment of the small bowel was sent to pathology. Grossly, a 2.0 cm tan-pink smooth round submucosal polyploid mass protruding into the lumen, mimicking a gastrointestinal stromal tumor, was identified. The tumor was hard and serially sectioned to reveal a white, calcified cut surface. Microscopically, the tumor appeared hypocellular and composed of scant spindle cells embedded in a dense, hyalinized and calcified collagenous stroma. Immunohistochemical stains for pan-cytokeratin, DOG1, desmin, S100, CD34, and MUC4 were negative, and a diagnosis of the calcifying fibrous tumor was rendered. This case provides a rare gross specimen image of calcifying fibrous tumor and highlights the importance of knowledge of rare entities in providing an accurate diagnosis for entities that can mimic other lesions.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors; Intestinal Polyps; Neoplasms, Fibrous Tissue.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures

References
-
- Rosenthal NS, Abdul-Karim FW. Childhood fibrous tumor with psammoma bodies. Clinicopathologic features in two cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988;112(8):798–800. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery E, Thomas GM, Fletcher CDM, Unni K, Mertens F. In: Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Fletcher CDM, Unni K, Martens F, editors. Lyon: IARC Press; 2002. Calcifying fibrous tumor. pp. 77–78. (World Health Organization Classification of Tumours).

