Concurrent severe hepatotoxicity and agranulocytosis induced by Polygonum multiflorum: A case report
- PMID: 36186172
- PMCID: PMC9516908
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9921
Concurrent severe hepatotoxicity and agranulocytosis induced by Polygonum multiflorum: A case report
Abstract
Background: Various types of drug-induced liver injury are induced by Polygonum multiflorum (PM); however, it rarely causes neutropenia. Herein, we report the case of a 65-year-old woman with concurrent severe hepatotoxicity and agranulocytosis induced by PM.
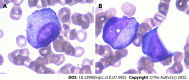
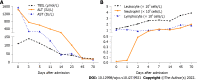
Case summary: A 65-year-old woman reported with severe hepatotoxicity and agranulocytosis 17 d after ingestion of PM. The results of the Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method demonstrated a highly probable relationship between hepatotoxicity and PM, with a total score of 10. The Naranjo algorithm results indicated that agranulocytosis had a probable relationship with PM, with an overall score of 6. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (for once), a steroid, compound glycyrrhizin, and polyene phosphatidylcholine therapy were initiated. After 15 d of treatment, there was a gradual improvement in liver biochemistry, leukocytes, and neutrophils levels.
Conclusion: Concurrent hepatotoxicity and agranulocytosis are rare and critical adverse drug reactions of PM, which should be highly valued.
Keywords: Agranulocytosis; Case report; Hepatotoxicity; Polygonum multiflorum.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polygonum multiflorum-Induced Liver Injury: Clinical Characteristics, Risk Factors, Material Basis, Action Mechanism and Current Challenges.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 13;10:1467. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01467. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31920657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eighteen cases of liver injury following ingestion of Polygonum multiflorum.Complement Ther Med. 2014 Feb;22(1):70-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2013.12.008. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Complement Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24559819
-
Concomitant agranulocytosis and hepatotoxicity after treatment with carbimazole.Ann Pharmacother. 2006 Nov;40(11):2059-63. doi: 10.1345/aph.1G720. Ann Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 17077174
-
Integrated spatially resolved metabolomics and network toxicology to investigate the hepatotoxicity mechanisms of component D of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115630. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115630. Epub 2022 Aug 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35987407
-
Polygonum multiflorum: Recent updates on newly isolated compounds, potential hepatotoxic compounds and their mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 May 10;271:113864. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113864. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33485980 Review.
References
-
- But PP, Tomlinson B, Lee KL. Hepatitis related to the Chinese medicine Shou-wu-pian manufactured from Polygonum multiflorum. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1996;38:280–282. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

