Synchronous primary duodenal papillary adenocarcinoma and gallbladder carcinoma: A case report and review of literature
- PMID: 36186218
- PMCID: PMC9516900
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i27.9790
Synchronous primary duodenal papillary adenocarcinoma and gallbladder carcinoma: A case report and review of literature
Abstract
Background: Synchronous primary cancers (SPCs) have become increasingly frequent over the past decade. However, the coexistence of duodenal papillary and gallbladder cancers is rare, and such cases have not been previously reported in the English literature. Here, we describe an SPC case with duodenal papilla and gallbladder cancers and its diagnosis and successful management.
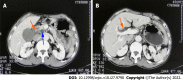
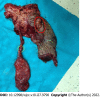
Case summary: A 68-year-old Chinese man was admitted to our hospital with the chief complaint of dyspepsia for the past month. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen performed at the local hospital revealed dilatation of the bile and pancreatic ducts and a space-occupying lesion in the duodenal papilla. Endoscopy revealed a tumor protruding from the duodenal papilla. Pathological findings for the biopsied tissue revealed tubular villous growth with moderate heterogeneous hyperplasia. Surgical treatment was selected. Macroscopic examination of this surgical specimen revealed a 2-cm papillary tumor and another tumor protruding by 0.5 cm in the gallbladder neck duct. Intraoperative rapid pathology identified adenocarcinoma in the gallbladder neck duct and tubular villous adenoma with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and local canceration in the duodenal papilla. After an uneventful postoperative recovery, the patient was discharged without complications.
Conclusion: It is essential for clinicians and pathologists to maintain a high degree of suspicion while evaluating such synchronous cancers.
Keywords: Case report; Duodenal papillary adenocarcinoma; Gallbladder carcinoma; Surgical treatment; Synchronous primary cancers.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adenocarcinoma of the minor duodenal papilla: report of a case.J Nippon Med Sch. 2013;80(2):165-70. doi: 10.1272/jnms.80.165. J Nippon Med Sch. 2013. PMID: 23657071
-
Intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasms (ICPN) of the gallbladder (neoplastic polyps, adenomas, and papillary neoplasms that are ≥1.0 cm): clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 123 cases.Am J Surg Pathol. 2012 Sep;36(9):1279-301. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318262787c. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22895264
-
Adenocarcinoma of the minor duodenal papilla: report of a case.Surg Today. 2011 Apr;41(4):568-71. doi: 10.1007/s00595-010-4314-0. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Surg Today. 2011. PMID: 21431496
-
[A case report of adenosquamous cell carcinoma of the duodenal papilla].Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2016;113(12):2067-2074. doi: 10.11405/nisshoshi.113.2067. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 27916775 Review. Japanese.
-
Synchronous hepatocellular carcinoma and gallbladder adenocarcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation: a case report and literature review.BMC Surg. 2020 Oct 20;20(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12893-020-00905-6. BMC Surg. 2020. PMID: 33081789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jin K, Xu J, Chen J, Chen M, Chen R, Chen Y, Chen Z, Cheng B, Chi Y, Feng ST, Fu D, Hou B, Huang D, Huang H, Huang Q, Li J, Li Y, Liang H, Lin R, Liu A, Liu J, Liu X, Lu M, Luo J, Mai G, Ni Q, Qiu M, Shao C, Shen B, Sheng W, Sun J, Tan C, Tan H, Tang Q, Tang Y, Tian X, Tong D, Wang X, Wang J, Wang W, Wang Y, Wu Z, Xue L, Yan Q, Yang N, Yang Y, Yang Z, Yin X, Yuan C, Zeng S, Zhang R, Yu X. Surgical management for non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms with synchronous liver metastasis: A consensus from the Chinese Study Group for Neuroendocrine Tumors (CSNET) Int J Oncol. 2016;49:1991–2000. - PubMed
-
- Ueno G, Ishikawa S, Ichikawa Y, Hagi T, Taniura N, Chong H, Kanazawa A, Takayama S, Nishihara M, Maruyama K, Shimada M, Lee K, Oka H, Maeda T. A case of synchronous cancer of the gall bladder, common bile duct, and the papilla of vater. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2014;41:1521–1523. - PubMed
-
- Seo YK, Choi JS. Endoscopic Papillectomy for Synchronous Major and Minor Duodenal Papilla Neuroendocrine Tumors. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018;72:217–221. - PubMed
-
- Parthasarathy S, Pottakkat B, Yootla M, Reddy SN, Reddy KM. Synchronous adenocarcinomas of the papilla major and minor. JOP. 2008;9:332–334. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

