The relationship between physical exercise and school adaptation of junior students: A chain mediating model
- PMID: 36186376
- PMCID: PMC9519055
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.977663
The relationship between physical exercise and school adaptation of junior students: A chain mediating model
Abstract
Objective: This study explores the relationship between physical exercise and school adaptation of junior middle school students and constructs a chain intermediary model through the intermediary role of psychological resilience and sports learning motivation.
Methods: Using the stratified cluster sampling method, 930 junior middle school students in Anhui Province were measured in group psychology by using the physical exercise rating scale, adolescent psychological resilience scale, physical learning motivation scale and school adaptation scale. The statistical software SPSS 23.0 and process plug-in were used for statistical processing, and the common method deviation test was carried out by Harman single-factor control method. Finally, the bootstrap sampling test method and process plug-in were used to test the significance of intermediary effect.
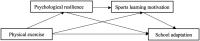
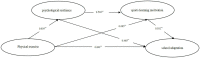
Results: (1) The direct prediction effect of physical exercise on school adaptation is remarkable (t = 4.60, p < 0.01); (2) psychological resilience and sports learning motivation are the intermediary variables of the relationship between physical exercise and school adaptation; (3) psychological resilience and sports learning motivation play a chain mediation role in the relationship between physical exercise and school adaptation. The intermediary effect is composed of three indirect effects: physical exercise → psychological resilience → school adaptation (95% Cl: 0.004, 0.041), physical exercise → physical learning motivation → school adaptation (95% Cl:0.019, 0.065), physical exercise → psychological resilience → physical learning motivation → school adaptation (95% Cl:0.002, 0.021).
Conclusions: Physical exercise can directly improve the school adaptation of junior middle school students, which can also affect junior middle school students' school adaptation indirectly through psychological resilience or sports learning motivation, and it can influence school adaptation through the chain mediation of psychological resilience and sports learning motivation.
Keywords: chain mediation; physical exercise; psychological resilience; school adaptation; sports learning motivation.
Copyright © 2022 Bai, Yao, Ma, Wang, Liu and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Y. M., Li Y. L., Xiao S. (2019). The relationship between interpersonal relationship and school adaptation of junior middle school students: A multiple intermediary model test. Special Educ. China 04, 83–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3728.2019.04.013 - DOI
-
- Cui N. (2008). A study on the relationship between school adaptation and self-concept of junior middle school students. Montana Ave: Southwest University.
-
- Fang J., Zhang M. Q. (2013). Analysis and comparison of simple mediation effect between parametric and nonparametric bootstrap methods. Psychol. Sci. 36, 722–727. doi: 10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2013.03.039 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources