Microfluidic wearable electrochemical sweat sensors for health monitoring
- PMID: 36186757
- PMCID: PMC9520469
- DOI: 10.1063/5.0116648
Microfluidic wearable electrochemical sweat sensors for health monitoring
Abstract
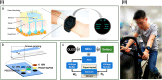
Research on remote health monitoring through wearable sensors has attained popularity in recent decades mainly due to aging population and expensive health care services. Microfluidic wearable sweat sensors provide economical, non-invasive mode of sample collection, important physiological information, and continuous tracking of human health. Recent advances in wearable sensors focus on electrochemical monitoring of biomarkers in sweat and can be applicable in various fields like fitness monitoring, nutrition, and medical diagnosis. This review focuses on the evolution of wearable devices from benchtop electrochemical systems to microfluidic-based wearable sensors. Major classification of wearable sensors like skin contact-based and biofluidic-based sensors are discussed. Furthermore, sweat chemistry and related biomarkers are explained in addition to integration of microfluidic systems in wearable sweat sensors. At last, recent advances in wearable electrochemical sweat sensors are discussed, which includes tattoo-based, paper microfluidics, patches, wrist band, and belt-based wearable sensors.
© 2022 Author(s).
Figures








Similar articles
-
Innovative Material-Based Wearable Non-Invasive Electrochemical Sweat Sensors towards Biomedical Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 May 14;14(10):857. doi: 10.3390/nano14100857. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidics by Additive Manufacturing for Wearable Biosensors: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jul 29;20(15):4236. doi: 10.3390/s20154236. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Wearable Microfluidic Sensors for Healthcare Monitoring.Small. 2020 Mar;16(9):e1903822. doi: 10.1002/smll.201903822. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Small. 2020. PMID: 31617311 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Skin-Interfaced Wearable Sweat Sensors: Opportunities for Equitable Personalized Medicine and Global Health Diagnostics.ACS Sens. 2023 Oct 27;8(10):3606-3622. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.3c01512. Epub 2023 Sep 25. ACS Sens. 2023. PMID: 37747817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fully Printed Wearable Microfluidic Devices for High-Throughput Sweat Sampling and Multiplexed Electrochemical Analysis.ACS Sens. 2021 Mar 26;6(3):1174-1186. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c02446. Epub 2021 Jan 31. ACS Sens. 2021. PMID: 33517662
Cited by
-
A Comparative Study of Optical Sensing Methods for Colourimetric Bio/Chemical Detection: Cost, Scale, and Performance.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 20;25(13):3850. doi: 10.3390/s25133850. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648109 Free PMC article.
-
Worth your sweat: wearable microfluidic flow rate sensors for meaningful sweat analytics.Lab Chip. 2025 Feb 25;25(5):1296-1315. doi: 10.1039/d4lc00927d. Lab Chip. 2025. PMID: 39878525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flexible and Wearable Biosensors for Monitoring Health Conditions.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 7;13(6):630. doi: 10.3390/bios13060630. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications and challenges of biomarker-based predictive models in proactive health management.Front Public Health. 2025 Aug 18;13:1633487. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1633487. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40900695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mukhopadhyay S. C., “Wearable sensors for human activity monitoring: A review,” IEEE Sens. J. 15(3), 1321–1330 (2015). 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2370945 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
