Rare, rarer, lung involvement in adult-onset Still's disease: A mini-review
- PMID: 36186767
- PMCID: PMC9522967
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.989777
Rare, rarer, lung involvement in adult-onset Still's disease: A mini-review
Abstract
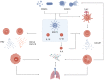
Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a polygenic systemic autoinflammatory disease which is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Pulmonary involvement is a rare, but serious complication of AOSD. As in AOSD, IL-1b, IL-18, and IL-6 dominate the molecular pathogenesis, which mediate a type 1 and type 3 inflammatory signature of the adaptive immune system. This is evidenced by the success of IL-1- and IL-6 inhibition in the management of AOSD. However, anaphylactic reactions to treatment with IL-1- or IL-6-inhibitors is currently being discussed as a potential trigger for lung involvement inf AOSD, while genetic risk factors have also been identified. Clinically, pulmonary involvement in AOSD can manifest in many different forms. Parenchymal inflammation with peripheral consolidations is the most frequent form while PAH is less common, but often very difficult to manage. This mini-review provides an overview of the pathophysiology as well as the clinical presentation and the diagnostic features of pulmonary involvement in AOSD.
Keywords: IL-1 blocking; IL-6 blocking; adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD); interstitial lung disease; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Copyright © 2022 Nies, Schneider and Krusche.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors MK and US have received speakers and consultant honoraria by Sobi, Novartis and Roche/Chugai. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nirmala N, Brachat A, Feist E, Blank N, Specker C, Witt M, et al. Gene-expression analysis of adult-onset Still's disease and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is consistent with a continuum of a single disease entity. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. (2015) 13:50. 10.1186/s12969-015-0047-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

