Are off-target effects of imatinib the key to improving beta-cell function in diabetes?
- PMID: 36187072
- PMCID: PMC9487420
- DOI: 10.48101/ujms.v127.8841
Are off-target effects of imatinib the key to improving beta-cell function in diabetes?
Abstract
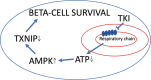
The small tyrosine kinase (TK) inhibitor imatinib mesylate (Gleevec, STI571) protects against both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, but as it inhibits many TKs and other proteins, it is not clear by which mechanisms it acts. This present review will focus on the possibility that imatinib acts, at least in part, by improving beta-cell function and survival via off-target effects on beta-cell signaling/metabolic flow events. Particular attention will be given to the possibility that imatinib and other TK inhibitors function as inhibitors of mitochondrial respiration. A better understanding of how imatinib counteracts diabetes will possibly help to clarify the pathogenic role of beta-cell signaling events and mitochondrial function, and hopefully leading to improved treatment of the disease.
Keywords: Pancreatic beta-cells; imatinib; mitochondria; type 1 diabetes; type 2 diabetes; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Upsala Medical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflicts of interest that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical