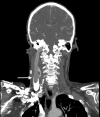
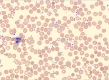
A woman presenting with facial droop
- PMID: 36187505
- PMCID: PMC9512762
- DOI: 10.1002/emp2.12827
A woman presenting with facial droop
Figures
References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. (Eds). World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, IARC Press, Lyon: 2008.
-
- Fenaux P, Simon M, Caulier MT, et al. Clinical course of essential thrombocythemia in 147 cases. Cancer. 1990; 66(3):549. - PubMed
-
- Wolanskyj AP, Lasho TL, Schwager SM, et al. JAK2 mutation in essential thrombocythaemia: clinical associations and long‐term prognostic relevance. Br J Haematol. 2005;131(2):208. - PubMed
-
- Tefferi A, Fonseca R, Pereira DL, et al. A long‐term retrospective study of young women with essential thrombocythemia. Mayo Clin Proc. 2001;76(1): 22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources