Electrical neuromodulation therapy for inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 36187600
- PMCID: PMC9516456
- DOI: 10.4291/wjgp.v13.i5.128
Electrical neuromodulation therapy for inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
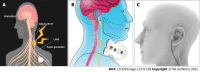
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It has financial and quality of life impact on patients. Although there has been a significant advancement in treatments, a considerable number of patients do not respond to it or have severe side effects. Therapeutic approaches such as electrical neuromodulation are being investigated to provide alternate options. Although bioelectric neuromodulation technology has evolved significantly in the last decade, sacral nerve stimulation (SNS) for fecal incontinence remains the only neuromodulation protocol commonly utilized use for GI disease. For IBD treatment, several electrical neuromodulation techniques have been studied, such as vagus NS, SNS, and tibial NS. Several animal and clinical experiments were conducted to study the effectiveness, with encouraging results. The precise underlying mechanisms of action for electrical neuromodulation are unclear, but this modality appears to be promising. Randomized control trials are required to investigate the efficacy of intrinsic processes. In this review, we will discuss the electrical modulation therapy for the IBD and the data pertaining to it.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Electrical neuromodulation; Inflammatory bowel disease; Neuromodulation; Sacral nerve stimulation; Tibial nerve stimulation; Ulcerative colitis; Vagus nerve stimulation.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Szigethy E, McLafferty L, Goyal A. Inflammatory bowel disease. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2010;19:301–318, ix. - PubMed
-
- Mayo Clinic gastroenterology and hepatology board review 95 ed. Oxford Medicine Online. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-Symptoms and causes-Mayo Clinic. [cited 6 July 2022]
-
- Cheng J, Shen H, Chowdhury R, Abdi T, Selaru F, Chen JDZ. Potential of Electrical Neuromodulation for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020;26:1119–1130. - PubMed
-
- Payne SC, Furness JB, Stebbing MJ. Bioelectric neuromodulation for gastrointestinal disorders: effectiveness and mechanisms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:89–105. - PubMed
-
- Erratum for the Research Article "Identification of Integrator-PP2A complex (INTAC), an RNA polymerase II phosphatase" by H. Zheng, Y. Qi, S. Hu, X. Cao, C. Xu, Z. Yin, X. Chen, Y. Li, W. Liu, J. Li, J. Wang, G. Wei, K. Liang, F. X. Chen, Y. Xu. Science. 2021;371 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

