Behavioral compliance with preventive health measures for students with and without hearing disability during COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36187678
- PMCID: PMC9523470
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.911671
Behavioral compliance with preventive health measures for students with and without hearing disability during COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Hearing loss affects over 1.5 billion individuals worldwide. Their disability and limited access to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic information make them suffer a greater degree than ordinary people. However, the quantitative studies on the implementation of behavior compliance with preventive health measures for vulnerable groups such as people with hearing disability were limited. The purpose of this study was to explore the compliance with pandemic-related protective health measures among people with hearing disability.
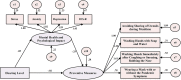
Design: A cross-sectional survey, population-based cohort study of students aged 12-26 years with and without hearing disability was conducted. Behavioral compliance with preventive health measures was collected from the general education institutions and special education schools using an online questionnaire. Logistic regression and structural equation model were used to determine the associations among the demographic variables, different degrees of mental health status and psychological impacts, and preventive health behaviors.
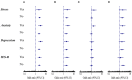
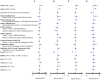
Results: Among 1,589 participants, 485 (30.5%) students are with hearing disability (SHD), and 1,104 (69.5%) students with normal hearing (SNH). The SHD has a significantly lower degree of behavioral compliance with the preventive health measures than SNH has. Hearing disability and anxiety [odds ratio (OR) = 1.54-1.76, p < 0.05] are risk factors for avoiding sharing of utensils during mealtime. Hearing disability, male sex, father's education level, mother's profession, bedtime after 11:00 p.m., anxiety, and depression (OR = 1.45-2.95, p < 0.05) are risk factors for hand hygiene. Male sex (OR = 2.13, p < 0.001) is risk factor and being aged below 18 years old (OR = 0.62, p = 0.03) is protective factor for wearing masks. Exercise (OR = 0.32-0.70, p < 0.01) is the most protective factor for preventive health behaviors. Mediating effect of mental health status and psychological impacts between hearing level and the compliance with the preventive health measures was -0.044 (95% CI: -0.068 to -0.027).
Conclusions: To reduce the risk of contraction, update pandemic information, essential communication services, extra assistance, and support should be provided to these disabled persons who are more susceptible to a public health emergency.
Keywords: COVID-19; health behaviors; hearing disability; preventive health measures; risk factors.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Liu, Xiao, Qu and Jen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

