Antiviral activity of mink interferon alpha expressed in the yeast Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 36187832
- PMCID: PMC9515496
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.976347
Antiviral activity of mink interferon alpha expressed in the yeast Pichia pastoris
Abstract
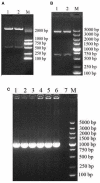
Many viruses can cause infections in mink, including canine distemper virus, mink enteritis virus, and Aleutian disease virus. Current treatments are ineffective, and these infections are often fatal, causing severe economic losses. As antiviral drugs may effectively prevent and control these infections, recent research has increasingly focused on antiviral interferons. Herein, the gene encoding a mature mink interferon alpha (MiIFN-α) was synthesized according to the P. pastoris preference of codon usage and a recombinant plasmid, pPICZαA-MiIFN-α, was constructed. pPICZαA-MiIFN-α was linearized and transformed into the P. pastoris X33 strain, and zeocin-resistant transformants were selected. Protein expression was induced by methanol. SDS-PAGE and western blot analyses showed that a 25-kDa fusion protein was expressed in the culture supernatant. Antiviral activity of the expressed protein was determined using cytopathic effect inhibition (CPEI). The purified MiIFN-α significantly inhibited the cytopathic effect of vesicular stomatitis virus with a green fluorescent protein (VSV-GFP) in F81 feline kidney cells, with an antiviral activity of 6.4 × 107 IU/mL; it also significantly inhibited MEV replication in F81 cells. MiIFN-α antiviral activity against VSV-GFP was significantly reduced on treatment with pH 4 and pH 10 conditions for 24 h (p < 0.01). Serum MiIFN-α concentrations in rat were measured using enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay; MiIFN-α concentrations in rat serum peaked at ~36 h after injection. A high dose of MiIFN-α was safe for use. There were no significant differences in body temperature, tissue changes, and lymphocyte, total white blood cell, and central granulocyte counts between the injected and control groups (p > 0.05). These findings lay a foundation for the large-scale production of recombinant MiIFNs.
Keywords: antiviral activity; interferon-alpha; mink; serum drug concentration; yeast expression.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zhang, Lu, Zou, Hu, Lian and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of the mink interferon-epsilon gene and its antiviral activity.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jan 27;9:972433. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.972433. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36776547 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and expression of mink (Neovison vison) interferon-γ gene and development of an antiviral assay.Res Vet Sci. 2015 Aug;101:93-8. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2015.06.012. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Res Vet Sci. 2015. PMID: 26267097
-
Identification and primary application of hybridomas cell secreting monoclonal antibodies against mink (Neovison vison) interferon-gamma.Cytokine. 2022 Feb;150:155777. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155777. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Cytokine. 2022. PMID: 34954494
-
[Secreted expression of porcine interferon beta in Pichia pastoris and its inhibition effect on the replication of Pseudorabies virus].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006 Jun;46(3):412-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16933611 Chinese.
-
[Alpha interferon, antiviral proteins and their value in clinical medicine].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1999 Nov-Dec;57(6):659-66. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1999. PMID: 10572214 Review. French.
References
-
- Zang ZX, Dan C, Zhou L, Zhang QY, Gui JF, Zhang YB. Function characterization and expression regulation of two different-sized 3' untranslated region-containing interferon genes from clone F of gibel carp Carassius auratus gibelio. Mol Immunol. (2020) 119:18–26. 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.01.004 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

