Comparative evaluation of eighth-generation bonding agent modified with 7% arginine and 0.12% chitosan for antibacterial property and microtensile bond strength
- PMID: 36187854
- PMCID: PMC9520639
- DOI: 10.4103/jcd.jcd_189_22
Comparative evaluation of eighth-generation bonding agent modified with 7% arginine and 0.12% chitosan for antibacterial property and microtensile bond strength
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare eighth-generation bonding agent (G-Premio BOND) modified with 7% arginine and 0.12% chitosan for antibacterial property and microtensile bond strength.
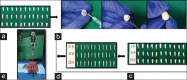
Methods: To evaluate antibacterial property, the sterile 96-microtiter plate was taken. The sidewalls of nine wells were coated with 15 μl of adhesive from each group. Suspension of Streptococcus mutans bacteria was placed on each group of adhesive and antibacterial property was checked using Spectrophotometer. Thirty-three healthy extracted premolars were taken and adhesive from each group was applied on the exposed surface of dentin, and the specimens were tested using a universal testing machine at crosshead speed of 1 mm/min.
Results: The least antibacterial efficacy was seen with unmodified eighth-generation bonding agent. This result was statistically significant when all study groups were compared. Microtensile bond strength was evaluated and the highest mean value (5.07) was seen with adhesive modified with 7% arginine, followed by adhesive modified with 0.12% chitosan (mean value: 4.14), and unmodified adhesive had the lowest mean bond strength value (4.07).
Conclusions: The eighth-generation bonding agent modified with 7% arginine and 0.12% chitosan showed antibacterial efficacy against S. mutans. In addition to this, they also had higher tensile bond strength values as compared to unmodified adhesive.
Keywords: Adhesive; antibacterial property; arginine; chitosan; microtensile bond strength.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Conservative Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of shear bond strength between fifth, sixth, seventh, and eighth generation bonding agents: An In Vitro study.Indian J Dent Res. 2020 Sep-Oct;31(5):752-757. doi: 10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_635_19. Indian J Dent Res. 2020. PMID: 33433514
-
Antibacterial Effect and Tensile Bond Strength of Self-etching Adhesive Resins with and without Methacryloyloxydodecylpyridinium Bromide: An in vitro Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018 Apr 1;19(4):409-414. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018. PMID: 29728545 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Microtensile Bond Strength of Three Adhesive Systems.Front Dent. 2022 Feb 6;19:8. doi: 10.18502/fid.v19i8.8725. eCollection 2022. Front Dent. 2022. PMID: 35937153 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of antibacterial inhibitory effect on Streptococcus mutans and tensile strength between chitosan-based bonding adhesives and commercial products.Indian J Dent Res. 2019 Jul-Aug;30(4):553-557. doi: 10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_236_18. Indian J Dent Res. 2019. PMID: 31745052
-
Assessment of antibacterial properties of newer dentin bonding agents: An in vitro study.Contemp Clin Dent. 2011 Jul;2(3):165-9. doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.86444. Contemp Clin Dent. 2011. PMID: 22090758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ganesh R. Dentin bonding agents – A review. Acta Sci Dent Sci. 2019;3:108–11.
-
- Stanislawczuk R, Pereira F, Muñoz MA, Luque I, Farago PV, Reis A, et al. Effects of chlorhexidine-containing adhesives on the durability of resin-dentine interfaces. J Dent. 2014;42:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Elaska SE. Antibacterial activity and adhesive properties of a chitosan – Containing dental adhesive in vitro. Quintessence Int. 2012;43:603–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
