High-throughput and automated screening for COVID-19
- PMID: 36188187
- PMCID: PMC9521367
- DOI: 10.3389/fmedt.2022.969203
High-throughput and automated screening for COVID-19
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has become a global challenge for the healthcare systems of many countries with 6 million people having lost their lives and 530 million more having tested positive for the virus. Robust testing and a comprehensive track and trace process for positive patients are essential for effective pandemic control, leading to high demand for diagnostic testing. In order to comply with demand and increase testing capacity worldwide, automated workflows have come into prominence as they enable high-throughput screening, faster processing, exclusion of human error, repeatability, reproducibility and diagnostic precision. The gold standard for COVID-19 testing so far has been RT-qPCR, however, different SARS-CoV-2 testing methods have been developed to be combined with high throughput testing to improve diagnosis. Case studies in China, Spain and the United Kingdom have been reviewed and automation has been proven to be promising for mass testing. Free and Open Source scientific and medical Hardware (FOSH) plays a vital role in this matter but there are some challenges to be overcome before automation can be fully implemented. This review discusses the importance of automated high-throughput testing, the different equipment available, the bottlenecks of its implementation and key selected case studies that due to their high effectiveness are already in use in hospitals and research centres.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-coV-2; automation; diagnostic; high-throughput.
© 2022 Jonguitud-Borrego, Malcı, Anand, Baluku, Webb, Liang, Barba-Ostria, Guaman, Hui and Rios-Solis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
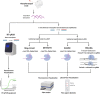
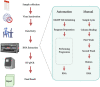
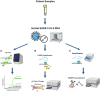

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of four different strategies for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the general population (CoV-Surv Study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a cluster-randomised, two-factorial controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 8;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04982-z. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33419461 Free PMC article.
-
Automated SARS-COV-2 RNA extraction from patient nasopharyngeal samples using a modified DNA extraction kit for high throughput testing.Ann Saudi Med. 2020 Sep-Oct;40(5):373-381. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2020.373. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Ann Saudi Med. 2020. PMID: 32954791 Free PMC article.
-
Automated sample-to-answer centrifugal microfluidic system for rapid molecular diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2.Lab Chip. 2022 Aug 23;22(17):3157-3171. doi: 10.1039/d2lc00242f. Lab Chip. 2022. PMID: 35670202
-
COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review of the RT-qPCR Method for Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jun 20;12(6):1503. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12061503. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlating WHO COVID-19 interim guideline 2020.5 and testing capacity, accuracy, and logistical challenges in Africa.Pan Afr Med J. 2021 May 31;39:89. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.39.89.27522. eCollection 2021. Pan Afr Med J. 2021. PMID: 34466191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An integrated microfluidic platform for nucleic acid testing.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024 May 23;10:66. doi: 10.1038/s41378-024-00677-6. eCollection 2024. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024. PMID: 38784376 Free PMC article.
-
Seeking Solutions for Inclusively Economic, Rapid, and Safe Molecular Detection of Respiratory Infectious Diseases: Comprehensive Review from Polymerase Chain Reaction Techniques to Amplification-Free Biosensing.Micromachines (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;16(4):472. doi: 10.3390/mi16040472. Micromachines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a large-scale rapid LAMP diagnostic testing platform for pandemic preparedness and outbreak response.Biol Methods Protoc. 2024 Nov 27;9(1):bpae090. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae090. eCollection 2024. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39664603 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of automated methods for COVID-19 PCR Master Mix preparation.SLAS Technol. 2024 Oct;29(5):100195. doi: 10.1016/j.slast.2024.100195. Epub 2024 Sep 28. SLAS Technol. 2024. PMID: 39349243 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and Temporal Analysis of Deletions Correlated to qRT-PCR Dropout in N Gene in Alpha, Delta and Omicron Variants.Viruses. 2023 Jul 26;15(8):1630. doi: 10.3390/v15081630. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37631974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler D, Mozsary C, Meydan C, Foox J, Rosiene J, Shaiber A, et al. Shotgun transcriptome, spatial omics, and isothermal profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals unique host responses, viral diversification, and drug interactions. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:1660. 10.1038/s41467-021-21361-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

