Liang-Ge decoction ameliorates acute lung injury in septic model rats through reducing inflammatory response, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and modulating host metabolism
- PMID: 36188538
- PMCID: PMC9523795
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.926134
Liang-Ge decoction ameliorates acute lung injury in septic model rats through reducing inflammatory response, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and modulating host metabolism
Abstract
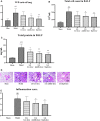
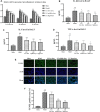
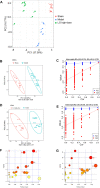
Liang-Ge decoction (LG) has been used in the treatment of early stage of spesis and can ameliorate sepsis-associated lung injury. However, the mechanism of LG on sepsis-associated lung injury remains unknown. In this study, we established a rat model of sepsis-associated lung injury using the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) method, and investigated the therapeutic effects of LG on lung injury in rats with sepsis. In addition, the anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects of LG on sepsis-associated lung injury model rats were evaluated. Besides, untargeted metabolomics was used to investigate the regulation of metabolites in rats with sepsis-associated lung injury after LG treatment. Our results showed that LG could decrease the wet/dry (W/D) ratio in lung and the total cell count and total protein concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in septic model rats. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining showed that LG reduced the infiltration of pro-inflammatory cells in lung. In addition, LG treatmment down-regulated the gene and protein expression of pro-inflammatory cytokins in lung tissue and BALF. The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) were increased and the level of methane dicarboxylic aldehyde (MDA) was decreased in lung tissue homogenate in septic model rats after LG treament. Moreover, the numbers of apoptotic cells in lung were reduced and the activity of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) in BALF was decreased in septic model rats after LG treament. Untargeted metabolomics analysis showed that LG treatment affected the levels of 23 metabolites in lung in septic model rats such as citric acid, methionine, threonine, alpha-ketoglutaric acid, and inositol, these metabolites were associated with the glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, cysteine and methionine metabolism, inositol phosphate metabolism and citrate cycle (TCA cycle) pathways. In conclusion, our study demonstrated the therapeutic effetcts of LG on sepsis-associated lung injury model rats. Moreover, LG could inhibit the inflammatory response, oxidative stress, apoptosis and regulate metabolites related to glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, cysteine and methionine metabolism, inositol phosphate metabolism and TCA cycle in lung in sepsis-associated lung injury model rats.
Keywords: apoptosis; inflammatory response; liang-Ge decoction; oxidative stress; sepsis-associated lung injury; untargeted metabolomics.
Copyright © 2022 He, Xi, Cui, Zhang, Huang, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Jian-Ti-Kang-Yi decoction alleviates poly(I:C)-induced pneumonia by inhibiting inflammatory response, reducing oxidative stress, and modulating host metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 6;13:979400. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.979400. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36147321 Free PMC article.
-
Liang-Ge Decoction Ameliorates Coagulation Dysfunction in Cecal Ligation and Puncture-Induced Sepsis Model Rats through Inhibiting PAD4-Dependent Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Apr 29;2023:5042953. doi: 10.1155/2023/5042953. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37159591 Free PMC article.
-
Senegenin Ameliorate Acute Lung Injury Through Reduction of Oxidative Stress and Inhibition of Inflammation in Cecal Ligation and Puncture-Induced Sepsis Rats.Inflammation. 2016 Apr;39(2):900-6. doi: 10.1007/s10753-016-0322-6. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26945584
-
[Role of Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in the protective effects of hydrogen against acute lung injury in septic mice].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 May;28(5):401-6. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 29920028 Chinese.
-
Hydrogen-rich saline ameliorates lung injury associated with cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis in rats.Exp Mol Pathol. 2015 Apr;98(2):268-76. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25746665 Review.
Cited by
-
Tocilizumab alleviated lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by improving PI3K/AKT pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8431-8442. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03786-9. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39797985
-
Comprehensive metabolomics study identifies SN-38 organ specific toxicity in mice.Sci Rep. 2025 May 12;15(1):16405. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01753-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40355563 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 exaggerates multiple organ injury, inflammation, and immune cell imbalance by activating the NF-κB pathway in sepsis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 7;14:1117285. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1117285. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36960276 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Supplementation with Bupleuri Radix Reduces Oxidative Stress Occurring during Growth by Regulating Rumen Microbes and Metabolites.Animals (Basel). 2024 Mar 17;14(6):927. doi: 10.3390/ani14060927. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540025 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of mitochondrial dysfunction induced pyroptosis in acute lung injury.Respir Res. 2024 Nov 7;25(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03028-1. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39511593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

