Zhuifeng tougu capsules inhibit the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and alleviate knee osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo experiments
- PMID: 36188596
- PMCID: PMC9521277
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.951860
Zhuifeng tougu capsules inhibit the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and alleviate knee osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo experiments
Abstract
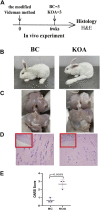
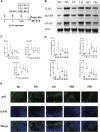
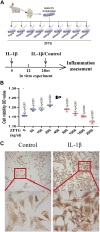
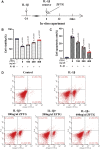
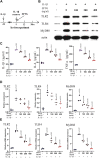
Background: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA), a chronic degenerative disease, is mainly characterized by destruction of articular cartilage and inflammatory reactions. At present, there is a lack of economical and effective clinical treatment. Zhuifeng Tougu (ZFTG) capsules have been clinically approved for treatment of OA as they relieve joint pain and inflammatory manifestations. However, the mechanism of ZFTG in KOA remains unknown. Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the effect of ZFTG on the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and its therapeutic effect on rabbits with KOA. Study design: In vivo, we established a rabbit KOA model using the modified Videman method. In vitro, we treated chondrocytes with IL-1β to induce a pro-inflammatory phenotype and then intervened with different concentrations of ZFTG. Levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ were assessed with histological observations and ELISA data. The effect of ZFTG on the viability of chondrocytes was detected using a Cell Counting Kit-8 and flow cytometry. The protein and mRNA expressions of TLR2, TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB were detected using Western blot and RT-qPCR and immunofluorescence observation of NF-κB p65 protein expression, respectively, to investigate the mechanism of ZFTG in inhibiting inflammatory injury of rabbit articular chondrocytes and alleviating cartilage degeneration. Results: The TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in rabbits with KOA was inhibited, and the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ in blood and cell were significantly downregulated, consistent with histological results. Both the protein and mRNA expressions of TLR2, TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB, and NF-κB p65 proteins in that nucleus decreased in the ZFTG groups. Moreover, ZFTG promotes the survival of chondrocytes and inhibits the apoptosis of inflammatory chondrocytes. Conclusion: ZFTG alleviates the degeneration of rabbit knee joint cartilage, inhibits the apoptosis of inflammatory chondrocytes, and promotes the survival of chondrocytes. The underlying mechanism may be inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kB signaling pathway and secretion of inflammatory factors.
Keywords: NF-κB; TLR4; Zhuifeng tougu capsules; inflammatory factors; innate immune; knee osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Li, Wu, Yan, Mi, Yi, Tan, Kuang and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
Author GK was employed by The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine and Hinye Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Barreto G., Senturk B., Colombo L., Bruck O., Neidenbach P., Salzmann G., et al. (2020). Lumican is upregulated in osteoarthritis and contributes to TLR4-induced pro-inflammatory activation of cartilage degradation and macrophage polarization. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 28 (1), 92–101. 10.1016/j.joca.2019.10.011 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

