Klotho: An Emerging Factor With Ergogenic Potential
- PMID: 36188832
- PMCID: PMC9397700
- DOI: 10.3389/fresc.2021.807123
Klotho: An Emerging Factor With Ergogenic Potential
Abstract
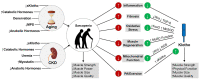
Sarcopenia and impaired cardiorespiratory fitness are commonly observed in older individuals and patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Declines in skeletal muscle function and aerobic capacity can progress into impaired physical function and inability to perform activities of daily living. Physical function is highly associated with important clinical outcomes such as hospitalization, functional independence, quality of life, and mortality. While lifestyle modifications such as exercise and dietary interventions have been shown to prevent and reverse declines in physical function, the utility of these treatment strategies is limited by poor widespread adoption and adherence due to a wide variety of both perceived and actual barriers to exercise. Therefore, identifying novel treatment targets to manage physical function decline is critically important. Klotho, a remarkable protein with powerful anti-aging properties has recently been investigated for its role in musculoskeletal health and physical function. Klotho is involved in several key processes that regulate skeletal muscle function, such as muscle regeneration, mitochondrial biogenesis, endothelial function, oxidative stress, and inflammation. This is particularly important for older adults and patients with CKD, which are known states of Klotho deficiency. Emerging data support the existence of Klotho-related benefits to exercise and for potential Klotho-based therapeutic interventions for the treatment of sarcopenia and its progression to physical disability. However, significant gaps in our understanding of Klotho must first be overcome before we can consider its potential ergogenic benefits. These advances will be critical to establish the optimal approach to future Klotho-based interventional trials and to determine if Klotho can regulate physical dysfunction.
Keywords: Klotho; chronic kidney disease (CKD); physical function; sarcopenia; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2022 Arroyo, Troutman, Moorthi, Avin, Coggan and Lim.
Conflict of interest statement
KL is Co-Founder of OVIBIO Corporation in Cambridge, MA. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

