Circulating pyruvate is a potent prognostic marker for critical COVID-19 outcomes
- PMID: 36189213
- PMCID: PMC9515795
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.912579
Circulating pyruvate is a potent prognostic marker for critical COVID-19 outcomes
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus-19 (COVID-19) disease is driven by an unchecked immune response to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus which alters host mitochondrial-associated mechanisms. Compromised mitochondrial health results in abnormal reprogramming of glucose metabolism, which can disrupt extracellular signalling. We hypothesized that examining mitochondrial energy-related signalling metabolites implicated in host immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection would provide potential biomarkers for predicting the risk of severe COVID-19 illness.
Methods: We used a semi-targeted serum metabolomics approach in 273 patients with different severity grades of COVID-19 recruited at the acute phase of the infection to determine the relative abundance of tricarboxylic acid (Krebs) cycle-related metabolites with known extracellular signaling properties (pyruvate, lactate, succinate and α-ketoglutarate). Abundance levels of energy-related metabolites were evaluated in a validation cohort (n=398) using quantitative fluorimetric assays.
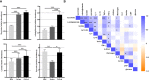
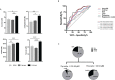
Results: Increased levels of four energy-related metabolites (pyruvate, lactate, a-ketoglutarate and succinate) were found in critically ill COVID-19 patients using semi-targeted and targeted approaches (p<0.05). The combined strategy proposed herein enabled us to establish that circulating pyruvate levels (p<0.001) together with body mass index (p=0.025), C-reactive protein (p=0.039), D-Dimer (p<0.001) and creatinine (p=0.043) levels, are independent predictors of critical COVID-19. Furthermore, classification and regression tree (CART) analysis provided a cut-off value of pyruvate in serum (24.54 µM; p<0.001) as an early criterion to accurately classify patients with critical outcomes.
Conclusion: Our findings support the link between COVID-19 pathogenesis and immunometabolic dysregulation, and show that fluorometric quantification of circulating pyruvate is a cost-effective clinical decision support tool to improve patient stratification and prognosis prediction.
Keywords: COVID-19; energy-related metabolites; fluorometric quantification; pyruvate; semi-targeted metebolomics.
Copyright © 2022 Ceperuelo-Mallafré, Reverté, Peraire, Madeira, Maymó-Masip, López-Dupla, Gutierrez-Valencia, Ruiz-Mateos, Buzón, Jorba, Vendrell, Auguet, Olona, Vidal, Rull and Fernández-Veledo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . COVID-19 therapeutic trial synopsis. World Heal Organ; (2020) p. 1–9. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/covid-19-therapeutic-trial-synop....
-
- Reverté L, Yeregui E, Olona M, Gutiérrez-Valencia A, Buzón MJ, Martí A, et al. Fetuin-a, inter-α-trypsin inhibitor, glutamic acid and ChoE (18:0) are key biomarkers in a panel distinguishing mild from critical coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes. Clin Transl Med (2022) 12:e704. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.704 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

