Adenosine signaling: Optimal target for gastric cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 36189223
- PMCID: PMC9523428
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1027838
Adenosine signaling: Optimal target for gastric cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
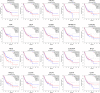
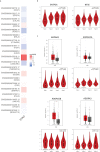
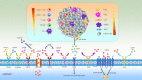
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common malignancy and leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Due to asymptomatic or only nonspecific early symptoms, GC patients are usually in the advanced stage at first diagnosis and miss the best opportunity of treatment. Immunotherapies, especially immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), have dramatically changed the landscape of available treatment options for advanced-stage cancer patients. However, with regards to existing ICIs, the clinical benefit of monotherapy for advanced gastric cancer (AGC) is quite limited. Therefore, it is urgent to explore an optimal target for the treatment of GC. In this review, we summarize the expression profiles and prognostic value of 20 common immune checkpoint-related genes in GC from Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) database, and then find that the adenosinergic pathway plays an indispensable role in the occurrence and development of GC. Moreover, we discuss the pathophysiological function of adenosinergic pathway in cancers. The accumulation of extracellular adenosine inhibits the normal function of immune effector cells and facilitate the effect of immunosuppressive cells to foster GC cells proliferation and migration. Finally, we provide insights into potential clinical application of adenosinergic-targeting therapies for GC patients.
Keywords: CD39; CD73; adenosine; gastric cancer; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Du and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adenosine signaling: Next checkpoint for gastric cancer immunotherapy?Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Oct;63:58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.07.023. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30075429 Review.
-
Advances in clinical immunotherapy for gastric cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Dec;1876(2):188615. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188615. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34403771 Review.
-
Progress and prospects of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced gastric cancer.Future Oncol. 2021 Apr;17(12):1553-1569. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-0829. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33397136 Review.
-
Application of immune checkpoint inhibitors in immunotherapy for gastric cancer.Immunotherapy. 2023 Feb;15(2):101-115. doi: 10.2217/imt-2022-0080. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Immunotherapy. 2023. PMID: 36597704 Review.
-
Immunotherapy of gastric cancer: Past, future perspective and challenges.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Feb;218:153322. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153322. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33422778 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in targeted therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive in advanced gastric cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Jun 15;16(6):2318-2334. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2318. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38994153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cell based immunotherapy against oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 13;15:1440764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1440764. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39192980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autologous CIK cells combined with chemotherapy as the first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer is safe and feasible.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 1;14:1267369. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1267369. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022664 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gastric Cancer Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Applications.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241271935. doi: 10.1177/15330338241271935. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39376170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[ARL67156, a small-molecule CD39 inhibitor, enhances natural killer cell cytotoxicity against gastric cancer cells in vitro and in nude mice].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Dec 20;43(12):2006-2014. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.12.03. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 38189385 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- He X, Wu L, Dong Z, Gong D, Jiang X, Zhang H, et al. . Real-time use of artificial intelligence for diagnosing early gastric cancer by magnifying image-enhanced endoscopy: A multicenter diagnostic study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc (2022) 95(4):671–8.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.11.040 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

