Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potential autoantigen for CD4 T cells in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 36189304
- PMCID: PMC9523785
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951281
Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potential autoantigen for CD4 T cells in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
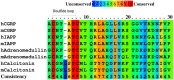
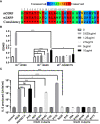
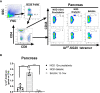
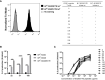
The calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a 37-amino acid neuropeptide with critical roles in the development of peripheral sensitization and pain. One of the CGRP family peptides, islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is an important autoantigen in type 1 diabetes. Due to the high structural and chemical similarity between CGRP and IAPP, we expected that the CGRP peptide could be recognized by IAPP-specific CD4 T cells. However, there was no cross-reactivity between the CGRP peptide and the diabetogenic IAPP-reactive T cells. A set of CGRP-specific CD4 T cells was isolated from non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. The T-cell receptor (TCR) variable regions of both α and β chains were highly skewed towards TRAV13 and TRBV13, respectively. The clonal expansion of T cells suggested that the presence of activated T cells responded to CGRP stimulation. None of the CGRP-specific CD4 T cells were able to be activated by the IAPP peptide. This established that CGRP-reactive CD4 T cells are a unique type of autoantigen-specific T cells in NOD mice. Using IAg7-CGRP tetramers, we found that CGRP-specific T cells were present in the pancreas of both prediabetic and diabetic NOD mice. The percentages of CGRP-reactive T cells in the pancreas of NOD mice were correlated to the diabetic progression. We showed that the human CGRP peptide presented by IAg7 elicited strong CGRP-specific T-cell responses. These findings suggested that CGRP is a potential autoantigen for CD4 T cells in NOD mice and probably in humans. The CGRP-specific CD4 T cells could be a unique marker for type 1 diabetes. Given the ubiquity of CGRP in nervous systems, it could potentially play an important role in diabetic neuropathy.
Keywords: CD4 T cells; CGRP; MHC; thiol regulation; type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Copyright © 2022 Li, Li, Wang, Zhang, Tomar and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Novel Tolerogenic Antibody Targeting Disulfide-Modified Autoantigen Effectively Prevents Type 1 Diabetes in NOD Mice.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 11;13:877022. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.877022. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032077 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting edge: CD4 T cells reactive to an islet amyloid polypeptide peptide accumulate in the pancreas and contribute to disease pathogenesis in nonobese diabetic mice.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 15;191(8):3990-4. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301480. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24043895 Free PMC article.
-
An insulin-IAPP hybrid peptide is an endogenous antigen for CD4 T cells in the non-obese diabetic mouse.J Autoimmun. 2017 Mar;78:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 29. J Autoimmun. 2017. PMID: 27802879 Free PMC article.
-
The physiology of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the islet compared with that of islet amyloid polypeptide (amylin).Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Jun 30;657:299-312. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb22777.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992. PMID: 1637089 Review.
-
Amylin, calcitonin gene-related peptide, calcitonin, and adrenomedullin: a peptide superfamily.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1997;11(2-3):167-239. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v11.i2-3.40. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1997. PMID: 9209829 Review.
Cited by
-
How inflammation dictates diabetic peripheral neuropathy: An enlightening review.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14477. doi: 10.1111/cns.14477. Epub 2023 Oct 5. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37795833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Novel Advances in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.J Diabetes. 2025 Aug;17(8):e70120. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.70120. J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40765373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mukherjee R, Wagar D, Stephens TA, Lee-Chan E, Singh B. Identification of CD4+ T cell-specific epitopes of islet-specific glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein: a novel beta cell autoantigen in type 1 diabetes. J Immunol (2005) 174(9):5306–15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.9.5306 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

