The use of the pediatric physeal slide-traction plate in the treatment of neer-horwitz grade IV proximal humeral fractures in children: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 36189382
- PMCID: PMC9515401
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.960541
The use of the pediatric physeal slide-traction plate in the treatment of neer-horwitz grade IV proximal humeral fractures in children: A case report and literature review
Abstract
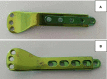
Background: Proximal humeral fractures (PHFs) are rare in children. Currently, the recommended surgical methods for severely displaced PHFs are closed reduction and percutaneous fixation using K-wires or intramedullary nailing, which can't provide firm internal fixation, especially for older and high-weight children. This study aimed to introduce a novel surgical approach, pediatric physeal slide-traction plate fixation (PPSP), for Neer-Horwitz grade IV PHFs in children.
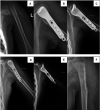
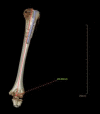
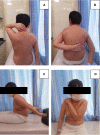
Case summary: A 9-year-old boy presented with left shoulder pain and swelling due to a car accident. Physical examination revealed a positive shoulder deformity and local tenderness. On physical examination, we palpated bone friction without vascular and nerve damage. Based on imaging findings, we diagnosed Neer-Horwitz grade IV PHF. In view of the patient's condition, we performed PPSP after careful communication with the patient's parents. After 22 months of follow-up, the patient's left shoulder function was satisfactory, and there was no restriction of activities.
Conclusion: According to previous studies, PPSP is only used for femur fractures. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first in the treatment for PHFs. Given the satisfactory outcomes, it is a safe and effective method and may provide a reference to cure analogous patients in the future.
Keywords: case report; children; literature review; pediatric physeal slide-traction plate; proximal humeral fracture.
© 2022 Qi, Jiang, Wang, Peng and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful Management of a Rare Pediatric Proximal Humerus Fracture-Dislocation Using K-Wire Fixation: A Case Report.J Orthop Case Rep. 2025 May;15(5):33-36. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2025.v15.i05.5546. J Orthop Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40351642 Free PMC article.
-
Elastic stable intramedullary nailing for displaced proximal humeral fractures in older children.J Child Orthop. 2008 Feb;2(1):15-9. doi: 10.1007/s11832-007-0070-0. Epub 2007 Dec 6. J Child Orthop. 2008. PMID: 19308598 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal humeral nail for treatment of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures in the elderly population: effective and safe in experienced hands.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021 May;31(4):769-777. doi: 10.1007/s00590-020-02832-x. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 33211233
-
Pediatric cervical kyphosis in the MRI era (1984-2008) with long-term follow up: literature review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2022 Feb;38(2):361-377. doi: 10.1007/s00381-021-05409-z. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Childs Nerv Syst. 2022. PMID: 34806157 Review.
-
[Reduction techniques for minimally invasive stabilization of proximal humeral fractures].Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2019 Feb;31(1):63-80. doi: 10.1007/s00064-018-0586-0. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 30683977 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Application of biodegradable implants in pediatric orthopedics: shifting from absorbable polymers to biodegradable metals.Bioact Mater. 2025 Apr 10;50:189-214. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.04.001. eCollection 2025 Aug. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40256329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neer CS, 2nd, Horwitz BS. Fractures of the proximal humeral epiphysial plate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (1965) 41:24–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

