The frequency and risk factors of major complications after thermal ablation of liver tumours in 2,084 ablation sessions
- PMID: 36189384
- PMCID: PMC9520062
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1010043
The frequency and risk factors of major complications after thermal ablation of liver tumours in 2,084 ablation sessions
Abstract
Background: To assess the frequency of major complications after thermal ablation of liver tumours and to determine risk factors for adverse events.
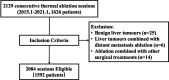
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted between January 2015 and January 2021. A total of 2,084 thermal ablation sessions in 1,592 patients with primary and metastatic liver tumours were evaluated. The frequency of major complications was evaluated according to the Society of Interventional Radiology Standards, and putative predictors of adverse events were analysed using simple and multivariate logistic regression.
Results: Thermal ablation-related mortality was 0.1% (2/2,084), with an overall major complication rate of 5.6% (117/2,084). The most frequent major complication was symptomatic pleural effusion (2.9%, 60/2,084). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that a total maximum diameter of lesions >3 cm, microwave ablation (MWA) and MWA combined with radiofrequency ablation, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and postoperative systemic inflammatory response syndrome were independent prognostic factors for major complications.
Conclusions: Thermal ablation of liver tumours is a safe procedure with an acceptable incidence of major complications. The risk factors identified in this study will help to stratify high-risk patients.
Keywords: liver tumours; major complications; risk factors; thermal ablation; ultrasound.
© 2022 Huang, Pang, Zeng, He, Zheng, Ge and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complications of thermal ablation of hepatic tumours: comparison of radiofrequency and microwave ablative techniques.Clin Radiol. 2013 Jun;68(6):608-15. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2012.12.008. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Clin Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23399463
-
Frequency and risk factors for major complications after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors in 1235 ablation sessions: a 15-year experience.Eur Radiol. 2021 May;31(5):3042-3052. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07409-0. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33125554 Free PMC article.
-
[Percutaneous cooled-tip microwave ablation under ultrasound guidance for primary liver cancer: analysis of major complications in 693 patients].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012 Dec;34(12):945-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2012.12.014. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23336384 Chinese.
-
The local efficacy and influencing factors of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation in colorectal liver metastases: a review of a 4-year experience at a single center.Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):36-43. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1528511. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019. PMID: 30489175 Review.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation in Liver Tumors: An Update.Oncologist. 2019 Oct;24(10):e990-e1005. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0337. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31217342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Organ Denervation: The Past, Present and Future.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 16;14(8):2746. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082746. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postoperative SIRS after thermal ablation of HCC: Risk factors and short-term prognosis.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 28;10(3):e25443. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25443. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38327471 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources