Ischemic stroke and intracranial hemorrhage in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36189498
- PMCID: PMC9527229
- DOI: 10.1177/02676591221130886
Ischemic stroke and intracranial hemorrhage in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is employed to support critically ill COVD-19 patients. The occurrence of ischemic stroke and intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), as well as the implementation of anticoagulation strategies under the dual influence of ECMO and COVID-19 remain unclear. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to describe the ischemic stroke, ICH and overall in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients receiving ECMO and summarize the anticoagulation regimens.
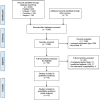
Methods: EMBASE, PubMed, Cochrane, and Scopus were searched for studies examining ischemic stroke, ICH, and mortality in COVID-19 patients supported with ECMO. The outcomes were incidences of ischemic stroke, ICH, overall in-hospital mortality and anticoagulation regimens. We calculated the pooled proportions and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to summarize the results.
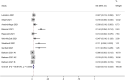
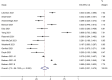
Results: We analyzed 12 peer-reviewed studies involving 6039 COVID-19 patients. The incidence of ischemic stroke had a pooled estimate of 2.2% (95% CI: 1.2%-3.2%). The pooled prevalence of ICH was 8.0% (95% CI: 6.3%-9.6%). The pooled estimate of overall in-hospital mortality was 40.3% (95% CI: 33.1%-47.5%). The occurrence of ICH was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients supported with ECMO than in other respiratory ECMO [relative risk=1.75 (95% CI: 1.00-3.07)]. Unfractionated heparin was the most commonly used anticoagulant, and anticoagulation monitoring practice varied among centers.
Conclusions: Ischemic stroke and ICH were common under the double "hit" of COVID-19 and ECMO. The prevalence of ICH was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients supported with ECMO than non-COVID-19 patients requiring ECMO. Individualized anticoagulation regimens may be a good choice to balance thrombosis and bleeding. More detailed research and further exploration are needed to clarify the underlying mechanism and clinical management decisions.
Keywords: COVID-19; anticoagulation; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; intracranial hemorrhage; ischemic stroke; overall in-hospital mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Reporting COVID-19 Cases into the ELSO Registry. Available from:https://www.elso.org/COVID19.aspx
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

