Neuropathology Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Autopsy Study
- PMID: 36190782
- PMCID: PMC9819270
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202205-453RL
Neuropathology Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Autopsy Study
Figures
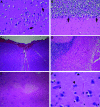
References
-
- Hopkins RO, Gale SD, Weaver LK. Brain atrophy and cognitive impairment in survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Brain Inj . 2006;20:263–271. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins RO, Weaver LK, Pope D, Orme JF, Bigler ED, Larson-LOHR V. Neuropsychological sequelae and impaired health status in survivors of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 1999;160:50–56. - PubMed
-
- Kim JS, Kim YJ, Kim M, Ryoo SM, Sohn CH, Ahn S, et al. The impact of severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome following cardiac arrest on neurologic outcomes. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag . 2021;11:96–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

