Gp35/50 mucin molecules of Trypanosoma cruzi metacyclic forms that mediate host cell invasion interact with annexin A2
- PMID: 36190932
- PMCID: PMC9529151
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010788
Gp35/50 mucin molecules of Trypanosoma cruzi metacyclic forms that mediate host cell invasion interact with annexin A2
Abstract
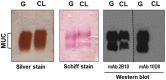
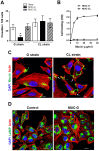
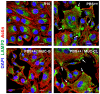
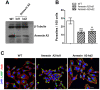
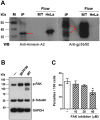
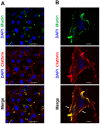
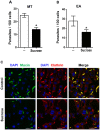
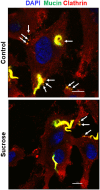
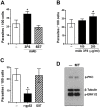
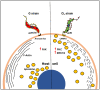
Host cell invasion is a critical step for infection by Trypanosoma cruzi, the agent of Chagas disease. In natural infection, T. cruzi metacyclic trypomastigote (MT) forms establish the first interaction with host cells. The gp35/50 mucin molecules expressed in MT have been implicated in cell invasion process, but the mechanisms involved are not well understood. We performed a series of experiments to elucidate the mode of gp35/50-mediated MT internalization. Comparing two parasite strains from genetically divergent groups, G strain (TcI) and CL strain (TcVI), expressing variant forms of mucins, we demonstrated that G strain mucins participate in MT invasion. Only G strain-derived mucins bound to HeLa cells in a receptor-dependent manner and significantly inhibited G strain MT invasion. CL strain MT internalization was not affected by mucins from either strain. HeLa cell invasion by G strain MT was associated with actin recruitment and did not rely on lysosome mobilization. To examine the involvement of annexin A2, which plays a role in actin dynamic, annexin A2-depleted HeLa cells were generated. Annexin A2-deficient cell lines were significantly more resistant than wild type controls to G strain MT invasion. In a co-immunoprecipitation assay, to check whether annexin A2 might be the receptor for mucins, protein A/G magnetic beads crosslinked with monoclonal antibody to G strain mucins were incubated with detergent extracts of MT and HeLa cells. Binding of gp35/50 mucins to annexin A2 was detected. Both G strain MT and purified mucins induced focal adhesion kinase activation in HeLa cells. By confocal immunofluorescence microscopy, colocalization of invading G strain MT with clathrin was visualized. Inhibition of clathrin-coated vesicle formation reduced parasite internalization. Taken together, our data indicate that gp35/50-mediated MT invasion is accomplished through interaction with host cell annexin A2 and clathrin-dependent endocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hayes MJ, Rescher U, Gerke V, Moss SE. Annexin-Actin interactions [Internet]. Traffic; 2004. pp. 571–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

