HAL-X: Scalable hierarchical clustering for rapid and tunable single-cell analysis
- PMID: 36191000
- PMCID: PMC9560626
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010349
HAL-X: Scalable hierarchical clustering for rapid and tunable single-cell analysis
Abstract
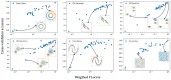
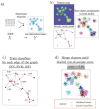
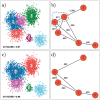
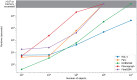
Data clustering plays a significant role in biomedical sciences, particularly in single-cell data analysis. Researchers use clustering algorithms to group individual cells into populations that can be evaluated across different levels of disease progression, drug response, and other clinical statuses. In many cases, multiple sets of clusters must be generated to assess varying levels of cluster specificity. For example, there are many subtypes of leukocytes (e.g. T cells), whose individual preponderance and phenotype must be assessed for statistical/functional significance. In this report, we introduce a novel hierarchical density clustering algorithm (HAL-x) that uses supervised linkage methods to build a cluster hierarchy on raw single-cell data. With this new approach, HAL-x can quickly predict multiple sets of labels for immense datasets, achieving a considerable improvement in computational efficiency on large datasets compared to existing methods. We also show that cell clusters generated by HAL-x yield near-perfect F1-scores when classifying different clinical statuses based on single-cell profiles. Our hierarchical density clustering algorithm achieves high accuracy in single cell classification in a scalable, tunable and rapid manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Bellman R. Dynamic Programming. Courier Corporation; 2013.
-
- Bouveyron C, Brunet-Saumard C. Model-based clustering of high-dimensional data: A review. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis. 2014;71:52–78. doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2012.12.008 - DOI
-
- Aggarwal CC, Reddy CK, editors. Data Clustering: Algorithms and Applications. 1st ed. Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

