A single helix repression domain is functional across diverse eukaryotes
- PMID: 36191192
- PMCID: PMC9564828
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2206986119
A single helix repression domain is functional across diverse eukaryotes
Abstract
The corepressor TOPLESS (TPL) and its paralogs coordinately regulate a large number of genes critical to plant development and immunity. As in many members of the larger pan-eukaryotic Tup1/TLE/Groucho corepressor family, TPL contains a Lis1 Homology domain (LisH), whose function is not well understood. We have previously found that the LisH in TPL-and specifically the N-terminal 18 amino acid alpha-helical region (TPL-H1)-can act as an autonomous repression domain. We hypothesized that homologous domains across diverse LisH-containing proteins could share the same function. To test that hypothesis, we built a library of H1s that broadly sampled the sequence and evolutionary space of LisH domains, and tested their activity in a synthetic transcriptional repression assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Using this approach, we found that repression activity was highly conserved and likely the ancestral function of this motif. We also identified key residues that contribute to repressive function. We leveraged this new knowledge for two applications. First, we tested the role of mutations found in somatic cancers on repression function in two human LisH-containing proteins. Second, we validated function of many of our repression domains in plants, confirming that these sequences should be of use to synthetic biology applications across many eukaryotes.
Keywords: LisH co-repressor; TPL; transcriptional repression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

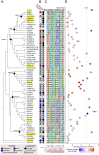
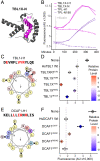
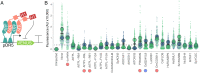
References
-
- Reynolds N., O’Shaughnessy A., Hendrich B., Transcriptional repressors: Multifaceted regulators of gene expression. Development 140, 505–512 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Courey A. J., Jia S., Transcriptional repression: The long and the short of it. Genes Dev. 15, 2786–2796 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Perissi V., Jepsen K., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Deconstructing repression: Evolving models of co-repressor action. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 109–123 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

