Obstructive Sleep Apnea-induced Endothelial Dysfunction Is Mediated by miR-210
- PMID: 36191258
- PMCID: PMC9896631
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202202-0394OC
Obstructive Sleep Apnea-induced Endothelial Dysfunction Is Mediated by miR-210
Abstract
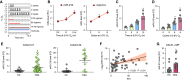
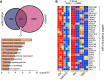
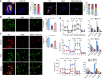
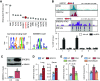
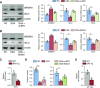
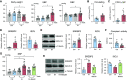
Rationale: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)-induced endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction contributes to OSA-related cardiovascular sequelae. The mechanistic basis of endothelial impairment by OSA is unclear. Objectives: The goals of this study were to identify the mechanism of OSA-induced EC dysfunction and explore the potential therapies for OSA-accelerated cardiovascular disease. Methods: The experimental methods include data mining, bioinformatics, EC functional analyses, OSA mouse models, and assessment of OSA human subjects. Measurements and Main Results: Using mined microRNA sequencing data, we found that microRNA 210 (miR-210) conferred the greatest induction by intermittent hypoxia in ECs. Consistently, the serum concentration of miR-210 was higher in individuals with OSA from two independent cohorts. Importantly, miR-210 concentration was positively correlated with the apnea-hypopnea index. RNA sequencing data collected from ECs transfected with miR-210 or treated with OSA serum showed a set of genes commonly altered by miR-210 and OSA serum, which are largely involved in mitochondrion-related pathways. ECs transfected with miR-210 or treated with OSA serum showed reduced [Formula: see text]o2 rate, mitochondrial membrane potential, and DNA abundance. Mechanistically, intermittent hypoxia-induced SREBP2 (sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2) bound to the promoter region of miR-210, which in turn inhibited the iron-sulfur cluster assembly enzyme and led to mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, the SREBP2 inhibitor betulin alleviated intermittent hypoxia-increased systolic blood pressure in the OSA mouse model. Conclusions: These results identify an axis involving SREBP2, miR-210, and mitochondrial dysfunction, representing a new mechanistic link between OSA and EC dysfunction that may have important implications for treating and preventing OSA-related cardiovascular sequelae.
Keywords: endothelium; miR-210; mitochondrial dysfunction; obstructive sleep apnea.
Figures

Comment in
-
miR-roring Changes in Blood: miR-210 Reflects Hypoxic Disease Dynamics in Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023 Feb 1;207(3):240-242. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202209-1709ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36201758 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Resta O, Foschino Barbaro MP, Bonfitto P, Talamo S, Mastrosimone V, Stefano A, et al. Hypercapnia in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Neth J Med . 2000;56:215–222. - PubMed
-
- Hoffstein V, Szalai JP. Predictive value of clinical features in diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep . 1993;16:118–122. - PubMed

