The triglyceride-glucose index as a novel marker associated with sarcopenia in non-diabetic patients on maintenance hemodialysis
- PMID: 36191303
- PMCID: PMC9543127
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2128373
The triglyceride-glucose index as a novel marker associated with sarcopenia in non-diabetic patients on maintenance hemodialysis
Abstract
Objective: Sarcopenia is a common complication in patients with end-stage kidney disease. Insulin resistance is present in non-diabetic patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) and is an important factor leading to sarcopenia. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, a reliable indicator for evaluating insulin resistance, is widely used in clinical practice. The present study investigated the association between the TyG index and sarcopenia in non-diabetic patients undergoing MHD.
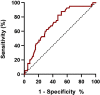
Methods: Relevant clinical data of non-diabetic patients undergoing MHD at our center were collected. The TyG index was calculated using the following formula: ln(fasting triglycerides(mg/dL)×fasting blood glucose(mg/dL)/2). Multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to evaluate the associations. The receiver-operating characteristic curve was used to analyze the predictive value of the TyG index in sarcopenia.
Results: Of the 142 patients undergoing MHD who were included, 75 (52.82%) were men, the mean age was 54.05 ± 13.97 years, and 40 (28.17%) patients satisfied the diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia. The TyG index of participants with sarcopenia was higher compared with those without sarcopenia (8.83 ± 0.45 vs. 8.49 ± 0.50, p < 0.001). The prevalence of sarcopenia increased with increasing TyG index tertile (T1, 8.51%; T2, 31.91%; T3, 43.75%; p = 0.001). Logistic regression analysis indicated that the TyG index was an independent risk factor for sarcopenia (odds ratio, 4.21 [95% confidence interval, 1.85-9.59], p = 0.001).
Conclusion: A higher TyG index was associated with an increased risk of sarcopenia in non-diabetic patients undergoing MHD; it may be used as a novel marker to reflect the presence of sarcopenia.
Keywords: Sarcopenia; insulin resistance; maintenance hemodialysis; non-diabetic; triglyceride-glucose index.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between the triglyceride-glucose index and coronary artery calcification in asymptomatic, non-diabetic patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2200849. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2200849. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37133817 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the triglyceride-glucose index and the risk of heart failure in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: a retrospective cohort study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 3;16:1544591. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1544591. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40248153 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the correlation between the serum triglyceride glucose index and the risk of death in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: a retrospective cohort study.PeerJ. 2025 Jan 2;13:e18781. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18781. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 39763694 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and the incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Apr 3;20(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01268-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33812373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effects of Personalized Exercise Prescriptions on Sarcopenia in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024 Apr;46(2):247-253. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.15588. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38686722 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and sarcopenia: a China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS)-based longitudinal analysis.J Health Popul Nutr. 2025 Aug 6;44(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-01030-x. J Health Popul Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40770777 Free PMC article.
-
Association of atherogenic index of plasma and triglyceride glucose-body mass index and sarcopenia in adults from 20 to 59: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 19;15:1437379. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1437379. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39224122 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Risk Factors of Sarcopenia in Patients with Maintenance Hemodialysis and Its Correlation with Emotional Status and Quality of Life.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Aug 1;17:3743-3751. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S469900. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39104383 Free PMC article.
-
The triglyceride glucose related index is an indicator of Sarcopenia.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 15;14(1):24126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75873-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39406884 Free PMC article.
-
Causal Associations Between Sarcopenia and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Womens Health. 2025 Feb 1;17:259-269. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S494910. eCollection 2025. Int J Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 39911357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang F, Yang C, Long J, et al. . Executive summary for the 2015 annual data report of the China kidney disease network (CK-NET). Kidney Int. 2019;95(3):501–505. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y-L, Zhang J-J, Li R-J, et al. . Prevalence of infections and antimicrobial use among hemodialysis outpatients: a prospective multicenter study. Semin Dial. 2020;33(2):156–162. - PubMed
-
- Lamarca F, Carrero JJ, Rodrigues JCD, et al. . Prevalence of sarcopenia in elderly maintenance hemodialysis patients: the impact of different diagnostic criteria. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18(7):710–717. 101007/s12603-014-0505-5 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
