Automated fracture screening using an object detection algorithm on whole-body trauma computed tomography
- PMID: 36192521
- PMCID: PMC9529907
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-20996-w
Automated fracture screening using an object detection algorithm on whole-body trauma computed tomography
Abstract
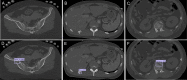
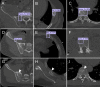
The emergency department is an environment with a potential risk for diagnostic errors during trauma care, particularly for fractures. Convolutional neural network (CNN) deep learning methods are now widely used in medicine because they improve diagnostic accuracy, decrease misinterpretation, and improve efficiency. In this study, we investigated whether automatic localization and classification using CNN could be applied to pelvic, rib, and spine fractures. We also examined whether this fracture detection algorithm could help physicians in fracture diagnosis. A total of 7664 whole-body CT axial slices (chest, abdomen, pelvis) from 200 patients were used. Sensitivity, precision, and F1-score were calculated to evaluate the performance of the CNN model. For the grouped mean values for pelvic, spine, or rib fractures, the sensitivity was 0.786, precision was 0.648, and F1-score was 0.711. Moreover, with CNN model assistance, surgeons showed improved sensitivity for detecting fractures and the time of reading and interpreting CT scans was reduced, especially for less experienced orthopedic surgeons. Application of the CNN model may lead to reductions in missed fractures from whole-body CT images and to faster workflows and improved patient care through efficient diagnosis in polytrauma patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automatic detection and classification of rib fractures based on patients' CT images and clinical information via convolutional neural network.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jun;31(6):3815-3825. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07418-z. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33201278
-
Automatic Detection and Classification of Rib Fractures on Thoracic CT Using Convolutional Neural Network: Accuracy and Feasibility.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Jul;21(7):869-879. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0651. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32524787 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of a Deep Learning Algorithm for the Detection of Rib Fractures on Whole-Body Trauma Computed Tomography.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Jul;21(7):891-899. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0653. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32524789 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for acute rib fracture detection in CT data: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Radiol. 2024 Feb 28;97(1155):535-543. doi: 10.1093/bjr/tqae014. Br J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38323515 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence fracture recognition on computed tomography: review of literature and recommendations.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023 Apr;49(2):681-691. doi: 10.1007/s00068-022-02128-1. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023. PMID: 36284017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence for Detection of Rib Fracture on X-ray and Computed Tomography Imaging: A Systematic Review.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Jan 27. doi: 10.1007/s10278-025-01412-x. Online ahead of print. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 39871041 Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultra-Low Dose CT Compared to Standard Dose CT for Identification of Fresh Rib Fractures by Deep Learning Algorithm.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Feb;38(1):124-133. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01027-8. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 39020151 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable Severity Scoring of Pelvic Trauma Through Automated Fracture Detection and Bayesian Inference.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025 Jan;44(1):130-141. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3428836. Epub 2025 Jan 2. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39037876 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Spinal Injury: A Narrative Review of Algorithms in Diagnosis and Prognosis.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 25;13(3):705. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030705. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in trauma orthopedics: Limitation and prospects.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jun 26;11(18):4231-4240. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i18.4231. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37449222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

