C5aR1 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer by EMT and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 36192575
- PMCID: PMC9873742
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-022-02956-y
C5aR1 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer by EMT and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant cancers in human, and its incidence increases gradually every year. Metastasis is an important factor leading to tumor development. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been proved to be closely related to tumor metastasis, yet its related mechanism in CRC remains to be explored.
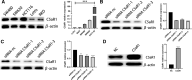
Methods: We obtained the differentially expressed gene C5aR1 with SETDB1 stable overexpression and knockdown cells by RNA-seq. Cell proliferation was tested by CCK8 and colony formation assay. Migration and invasion of CRC cells were determined by the wound healing and transwell invasion assay. The potential pathway of C5aR1 in CRC was preliminarily studied by western blotting.
Results: Sequencing results showed that C5aR1 was the most differentially expressed gene. By changing the expression of C5aR1 in CRC cells, this study found that C5aR1 promoted the proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion of CRC cells in vitro. C5aR1 accelerated the EMT process and the expression of C5aR1 altered the molecular expression of key proteins in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusion: C5aR1 promotes the development of CRC and accelerates the EMT process. Furthermore, C5aR1 may involve in the regulation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in CRC.
Keywords: C5aR1; CRC; EMT; RNA-seq; Wnt/β-catenin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

