Development of a Novel Inflammatory-Associated Gene Signature and Immune Infiltration Patterns in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
- PMID: 36193061
- PMCID: PMC9526649
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2481071
Development of a Novel Inflammatory-Associated Gene Signature and Immune Infiltration Patterns in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Abstract
Background: Both inflammatory factors and immune response play important roles in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). However, a comprehensive analysis of interaction between inflammatory response-associated genes (IRGs) and immune microenvironment in patients with IDD remains lacking. Hence, the current research is aimed at investigating the correlations between IRG signatures and immune cells in the progression of IDD.
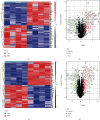
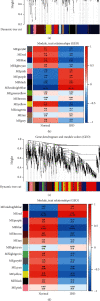
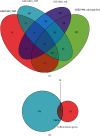
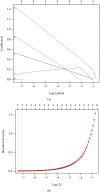
Methods: The expression profiles (GSE27494 and GSE41883) and IRGs were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and Molecular Signature Database (MSigDB), respectively. Weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA) and differential expression analysis were used to identify the pivotal modules and common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with IDD. Subsequently, we retrieved differentially expressed IRGs (DE-IRGs) by intersecting IRGs and DEGs for enrichment analysis. Next, LASSO regression analyses were performed to screen optimal marker genes for IDD prediction. Additionally, we validated differences DE-IRGs between IDD patients and controls in GSE150408. Finally, the infiltration alteration of immune cells was evaluated by the CIBERSORT, and the correlation between diagnostic markers and infiltrating immune cells was analyzed.
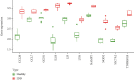
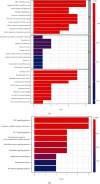
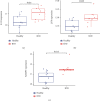
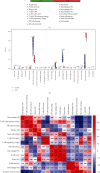
Results: A total of 10 upregulated differentially expressed inflammatory genes were identified that were obviously related to progression of IDD. Functional analysis results revealed that DE-IRGs were mainly enriched in signaling pathways TNF, IL-17, NOD-like receptor, and NF-kappa B pathway. A five-gene signature that consisted of IL-1β, LIF, LYN, NAMPT, and SLC7A2 was constructed by the LASSO Cox regression. IL1B, LYN, and NAMPT were further validated as optimal candidate genes in the pathophysiology of IDD. In addition, there was a remarkable immune cell infiltration difference between the healthy and IDD groups. The proportions for dendritic cells activated, mast cells activated, and neutrophils in the IDD group were significantly higher than those in the normal group, while the proportion of some cells was lower than that of the normal group, such as T cell CD4 memory resting, NK cells activated, and macrophage M0. Furthermore, correlation analysis indicated IL-1β, LYN, and NAMPT were closely implicated with immune cell infiltration in IDD development.
Conclusions: We explored an association between inflammatory response-associated signature and immune infiltration in IDD and validated that IL-1β, LYN, and NAMPT might serve as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for IDD in the future.
Copyright © 2022 Tao Lan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose in relation to this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of SMIM1 and SEZ6L2 as Potential Biomarkers for Genes Associated with Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Pyroptosis.Dis Markers. 2022 May 7;2022:9515571. doi: 10.1155/2022/9515571. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. Retraction in: Dis Markers. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9806892. doi: 10.1155/2023/9806892. PMID: 35578687 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Identification of cellular senescence-related genes and immune cell infiltration characteristics in intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 12;15:1439976. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1439976. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39328407 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK8 and CAPN1 as potential biomarkers of intervertebral disc degeneration overlapping immune infiltration, autophagy, and ceRNA.Front Immunol. 2023 May 30;14:1188774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188774. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37325630 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated identification of key immune related genes and patterns of immune infiltration in calcified aortic valvular disease: A network based meta-analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 21;13:971808. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.971808. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36212153 Free PMC article.
-
The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110660. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110660. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32853910 Review.
Cited by
-
ANGPTL4 May Regulate the Crosstalk Between Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Combined Analysis of Bioinformatics and Rat Models.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 27;16:6361-6384. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S426439. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38161353 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the characteristics of mild intervertebral disc degeneration at various age stages using single-cell genomics.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 2;12:1409287. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1409287. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39015652 Free PMC article.
-
GREM1, LRPPRC and SLC39A4 as potential biomarkers of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bioinformatics analysis based on multiple microarray and single-cell sequencing data.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Sep 12;24(1):729. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06854-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37700277 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Oxidative Stress in the Diagnosis and Subtype Classification of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Biochem Genet. 2024 Feb;62(1):193-207. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10412-x. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37314550
-
The Significance of MAPK Signaling Pathway in the Diagnosis and Subtype Classification of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.JOR Spine. 2025 Mar 24;8(1):e70060. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70060. eCollection 2025 Mar. JOR Spine. 2025. PMID: 40134951 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

