The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase SYVN1 Plays an Antiapoptotic Role in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by Regulating Mitochondrial Fission
- PMID: 36193086
- PMCID: PMC9526636
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3639302
The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase SYVN1 Plays an Antiapoptotic Role in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by Regulating Mitochondrial Fission
Abstract
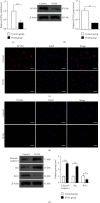
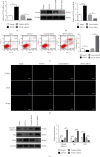
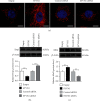
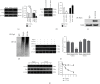
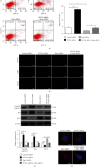
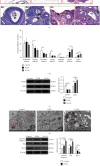
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disorders among premenopausal women. PCOS is accompanied by many other reproductive, endocrinal, and metabolic disorders thus amassing the difficulties encountered by the women affected. However, there is limited information on its molecular etiology. Synoviolin (SYVN1) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is thought to participate in the pathology of PCOS. However, the expression and function of SYVN1 in PCOS are unknown. In this study, we found that downregulation of SYVN1 expression was followed by increased apoptosis in the granulosa cells (GCs) of patients with PCOS. Subsequent in vitro experiments indicated that the overexpression of SYVN1 inhibited apoptosis and mitochondrial fission. Furthermore, using immunoprecipitation and western blotting, we identified that SYVN1 promoted the degradation of Drp1 via the proteasome-dependent pathway. Additionally, we generated a PCOS model in female Sprague Dawley rats and treated them with an SYVN1 inhibitor, LS-102. We observed that the inhibition of SYVN1 increased Drp1 levels and exacerbated the degeneration of GCs in the PCOS rat model. Finally, in vitro and in vivo experiments showed that SYVN1 inhibits apoptosis and mitochondrial fission by promoting Drp1 degradation in GCs. These results highlight the function of SYVN1 in PCOS and provide a potential target for the clinical treatment of PCOS.
Copyright © 2022 Lihua Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dihydrotestosterone induces reactive oxygen species accumulation and mitochondrial fission leading to apoptosis of granulosa cells.Toxicology. 2024 Dec;509:153958. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2024.153958. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Toxicology. 2024. PMID: 39332622
-
SYVN1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of MSH3 promotes the apoptosis of lens epithelial cells.FEBS J. 2022 Sep;289(18):5682-5696. doi: 10.1111/febs.16447. Epub 2022 Apr 3. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 35334159
-
Addressing the role of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome and the putative therapeutic effects of its selective inhibition in a preclinical model.Metabolism. 2021 Jun;119:154749. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154749. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Metabolism. 2021. PMID: 33722534
-
microRNA-194 is increased in polycystic ovary syndrome granulosa cell and induce KGN cells apoptosis by direct targeting heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Nov 23;19(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00850-w. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34814928 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase SYVN1 as a promising therapeutic target for diverse human diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2025 Feb;212:107603. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2025.107603. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Pharmacol Res. 2025. PMID: 39818260 Review.
Cited by
-
Casting Light on the Janus-Faced HMG-CoA Reductase Degradation Protein 1: A Comprehensive Review of Its Dualistic Impact on Apoptosis in Various Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):6842-6863. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03994-z. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38356096 Review.
-
Control of Mitochondrial Activity by the Ubiquitin Code in Health and Cancer.Cells. 2023 Jan 5;12(2):234. doi: 10.3390/cells12020234. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted functions of Drp1 in hypoxia/ischemia-induced mitochondrial quality imbalance: from regulatory mechanism to targeted therapeutic strategy.Mil Med Res. 2023 Oct 13;10(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00482-8. Mil Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37833768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Mendelian randomization and single-cell analysis insights.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Feb 19;18(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01617-2. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 39972362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zadeh Modarres S., Heidar Z., Foroozanfard F., Rahmati Z., Aghadavod E., Asemi Z. The effects of selenium supplementation on gene expression related to insulin and lipid in infertile polycystic ovary syndrome women candidate for in vitro fertilization: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biological Trace Element Research . 2018;183(2):218–225. doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-1148-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

