A stochastically perturbed co-infection epidemic model for COVID-19 and hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 36193119
- PMCID: PMC9517998
- DOI: 10.1007/s11071-022-07899-1
A stochastically perturbed co-infection epidemic model for COVID-19 and hepatitis B virus
Abstract
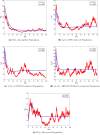
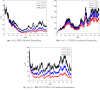
A new co-infection model for the transmission dynamics of two virus hepatitis B (HBV) and coronavirus (COVID-19) is formulated to study the effect of white noise intensities. First, we present the model equilibria and basic reproduction number. The local stability of the equilibria points is proved. Moreover, the proposed stochastic model has been investigated for a non-negative solution and positively invariant region. With the help of Lyapunov function, analysis was performed and conditions for extinction and persistence of the disease based on the stochastic co-infection model were derived. Particularly, we discuss the dynamics of the stochastic model around the disease-free state. Similarly, we obtain the conditions that fluctuate at the disease endemic state holds if . Based on extinction as well as persistence some conditions are established in form of expression containing white noise intensities as well as model parameters. The numerical results have also been used to illustrate our analytical results.
Keywords: Extinction; Numerical results; Persistence; Stability analysis; Stochastic co-infection model.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A stochastic SACR epidemic model for HBV transmission.J Biol Dyn. 2020 Dec;14(1):788-801. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2020.1833993. J Biol Dyn. 2020. PMID: 33073738
-
Dynamic modeling and analysis of Hepatitis B epidemic with general incidence.Math Biosci Eng. 2023 Apr 20;20(6):10883-10908. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023483. Math Biosci Eng. 2023. PMID: 37322965
-
A stochastic model for the transmission dynamics of hepatitis B virus.J Biol Dyn. 2019 Dec;13(1):328-344. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2019.1600750. J Biol Dyn. 2019. PMID: 30947627
-
Analysis of a stochastic HBV infection model with delayed immune response.Math Biosci Eng. 2021 Jun 10;18(5):5194-5220. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021264. Math Biosci Eng. 2021. PMID: 34517484
-
Threshold dynamics of a stochastic SIHR epidemic model of COVID-19 with general population-size dependent contact rate.Math Biosci Eng. 2022 Feb 21;19(4):4217-4236. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022195. Math Biosci Eng. 2022. PMID: 35341295
Cited by
-
Analysis of HBV and COVID-19 Coinfection Model with Intervention Strategies.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 29;2023:6908757. doi: 10.1155/2023/6908757. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811291 Free PMC article.
-
The stability analysis of a co-circulation model for COVID-19, dengue, and zika with nonlinear incidence rates and vaccination strategies.Healthc Anal (N Y). 2023 Nov;3:100151. doi: 10.1016/j.health.2023.100151. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Healthc Anal (N Y). 2023. PMID: 36883137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J, Tian X. Global stability of a delay differential equation of hepatitis B virus infection with immune. Electron. J. Differ. Equ. 2013;2013(94):1–11.
-
- Upadhyay RK, Iyengar SR. Spatial Dynamics and Pattern Formation in Biological Populations. London: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
