Efficacy of Fuyuan Xingshen Decoction Combined with Butylphthalide Sodium Chloride Injection in the Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction and Its Effect on Hemodynamics
- PMID: 36193139
- PMCID: PMC9526653
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2402040
Efficacy of Fuyuan Xingshen Decoction Combined with Butylphthalide Sodium Chloride Injection in the Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction and Its Effect on Hemodynamics
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Efficacy of Fuyuan Xingshen Decoction Combined with Butylphthalide Sodium Chloride Injection in the Treatment of Acute Cerebral Infarction and Its Effect on Hemodynamics.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9754181. doi: 10.1155/2023/9754181. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38093886 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to determine the curative effect of Fuyuan Xingshen Decoction combined with butylphthalide sodium chloride injection in acute cerebral infarction (ACI) treatment and its effect on hemodynamics.
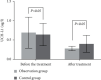
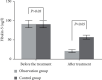
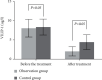
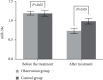
Methods: In our hospital, a total of 84 ACI patients from May 2020 to February 2022 were randomly divided into two groups: observation and control (n = 42 each). Fuyuan Xingshen Decoction in combination with butylphthalide sodium chloride injection was provided to the observation group, while the control group received butylphthalide sodium chloride injection alone. Both groups' clinical efficacy was observed. Before and after treatment, the neurological function of the two groups was evaluated using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), while the daily living ability of both groups was determined using the Barthel index rating scale. Both groups were investigated for their cognitive function, before and after treatment, by using the Mini-Cog scale and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scale. The pulsatility index (PI), peak velocity (Vp), and mean velocity (Vm) of intracranial arteries were measured by transcranial Doppler ultrasonography before and after treatment. The levels of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase-1 (UCH-L1), Fibulin-5, and visinin-like protein-1 (VILIP-1) in serum and the expression levels of miR-34c, miR-25, and miR-182 in peripheral blood of the two groups were compared. Both groups were observed for the incidence of adverse reactions.
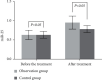
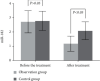
Results: Compared with the control (71.43%), the observation group exhibited a significantly higher effective rate of around 90.48%. In the observation group, the improvement in NIHSS, Barthel index, Mini-cog, and MoCA scores; hemodynamic indexes including Vp, PI, and Vm; serum UCH-L1, Fibulin-5, and VILIP-1 levels; and the miR-34c, miR-25, and miR-182 expression levels in peripheral blood was better than the control group, with significant difference (all P < 0.05). The incidence of adverse reactions between the groups demonstrated no significant differences (P > 0.05).
Conclusions: Fuyuan Xingshen Decoction combined with butylphthalide sodium chloride injection can effectively improve patients' daily living ability, neurological function, cognitive function, and cerebral hemodynamics in the treatment of ACI, with good effect and safety.
Copyright © 2022 Jiangang Ji et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang L. D., Xu Z. M., Liang X., et al. Overview of systematic reviews of Panax notoginseng saponins in treatment of acute cerebral infarction. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi . 2021;46(12):2963–2971. - PubMed
-
- Wang D. L., Li X. Retrospective analysis of neurological deficit and blood lipid levels in acute cerebral infarction [C]//CCCD2015 15th China cerebrovascular disease conference. 2015. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4624572/
-
- Yang D. N., Zhang D., Yu J. J. Effects of butylphthalide injection combined with edaravone on cytokines, vascular endothelial function and oxidative stress in elderly patients with acute cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Gerontology . 2021;41(3):p. 4.
-
- Zhu J. Q. Study on the clinical effect of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of cerebral infarction. Oriental Medicinal Diet . 2019;22:p. 230.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

